Developer Guide
The design documentation is in general for anyone who wants to understand the system architecture and design of Pac. The following groups are in particular the intended audience of the document.
- PAC project managers
- PAC developers
- PAC software testers
Table of Contents
- Setting Up
1.1 Requirements
1.2 Startup using Command Line
1.3 Startup using Jar - Design
2.1 Architecture
2.2 UI component
2.3 Command component
2.4 Parse component
2.5 Storage component - Implementation of Features
3.1 Event
3.2 Calendar
3.3 Attendance
3.4 Performance
3.5 Student List Collection
3.6 Help
Appendix A: Target User Profile
Appendix B: Value Proposition
Appendix C: Non-functional requirements
Appendix D: User Stories
Appendix E: Instructions for Manual Testing
Glossary
1. Setting Up
1.1 Requirements
- Ensure you have Java 11 or above installed in your Computer.
- Download the latest PAC.jar from here.
- Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for this application.
- Type
java -jar PAC-2.1.jarto start the application. - You should see this screen if everything is successful.
1.2 Startup using Command Line
- Open your terminal.
- Navigate to the home folder containing PAC.
- cd followed by the file path into the terminal as shown below
- Type
java -jarfollowed by the name of the jar file and press Enter.
1.3 Startup using JAR
- Open home folder containing PAC.
- Run the packaged JAR file by double clicking it
and a window should appear in a few seconds.
- Once opened, type in the command when prompted and press Enter.
2. Design
2.1 Overall Architecture
This section presents the architecture of PAC. It explains the architecture of main components of PAC.
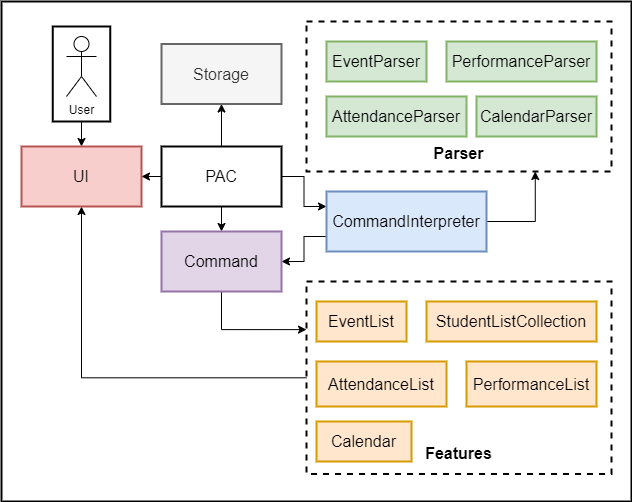
Overall architecture design of Pac
The Pac component contains all other components in the application.
UI: reads user input, and prints output in pre-defined format.Storage: loads/stores all events (in EventList) and all student lists (in StudentListCollection).CommandInterpreter: Determines category and type of command from user input.- Various
Parser: Breaks down user input to obtain command parameters. - Various
Features: stores their respective objects during runtime.EventList: stores all events during runtime.StudentListCollection: stores all student lists during runtime.AttendanceList: stores all attendances related to anEvent.PerformanceList: stores all performances related to anEvent.Calendar: shows all events in calendar form.
2.2 UI component
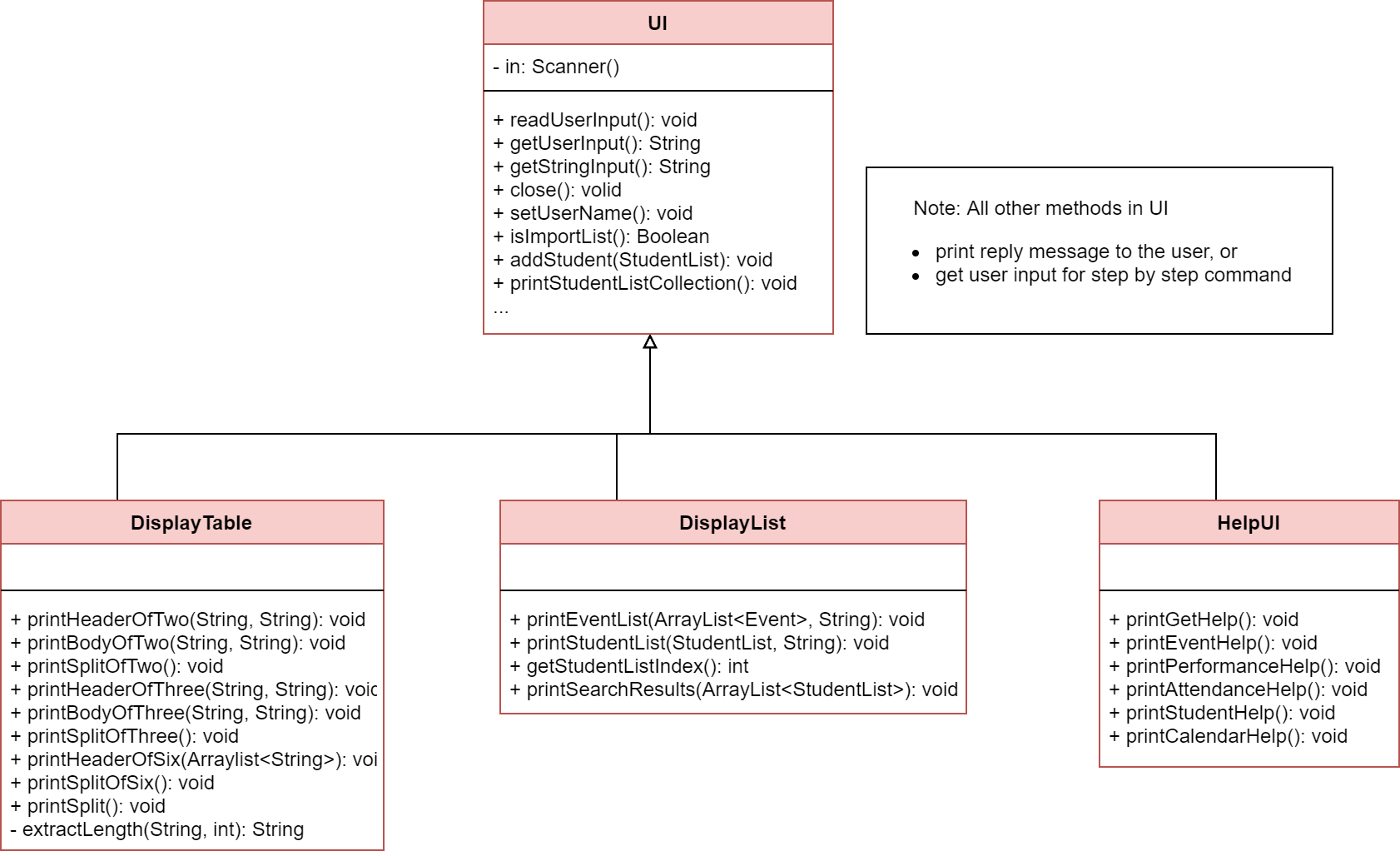
Class diagram of the UI component
UI is the main class handles user display, which includes reading user input and printing information
back to the user on command-line.
Besides the normal command line messages, there are three subclasses of UI:
- DisplayList and DisplayTable: to specifically print the list and table interface to user.
- HelpUI: to print the summary of command format to user.
2.3 Command component
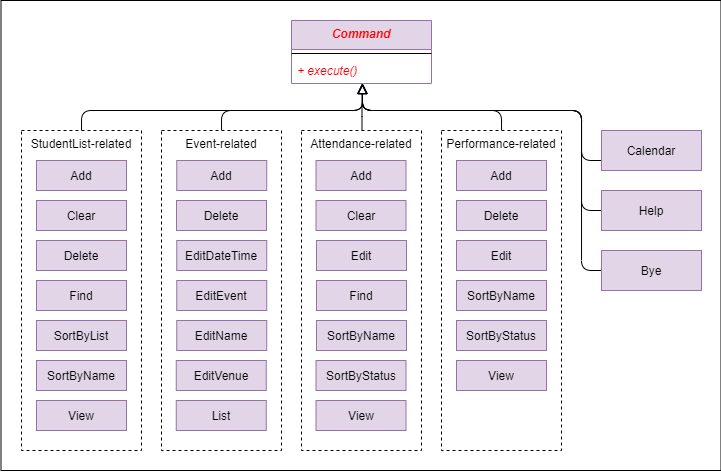
Class diagram of the Command component
The diagram above shows all commands in this program, which are grouped under
their own categories (i.e. StudentList-related, Event-related,
Attendance-related, Performance-related). All these commands inherit the
base Command abstract class and utilize its abstract execute() method.
They are created and executed when the user inputs a corresponding command.
2.4 Parser component
There are total of four Parser classes as shown below. Each Parser class correspond to a feature of Pac.
| Parser | Created by |
|---|---|
| EventParser | EventCommandInterpreter |
| CalenderParser | CalendarCommandInterpreter |
| PerformanceParser | Step-by-step command at performance-related command classes |
| AttendanceParser | Step-by-step command at attendance-related command classes |
A Parser class is created when a user input contains data to be stored or used in certain features.
2.5 Storage component
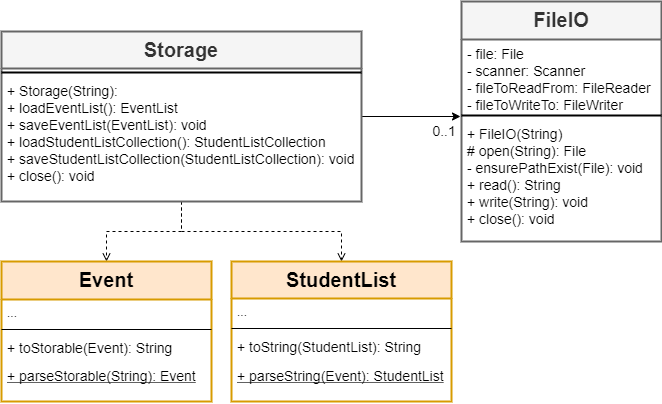
Class diagram of the Storage component
On startup, Pac instantiates two Storage objects (eventStorage and
studentListStorage) to load and save Event and StudentList objects
respectively. Each event requires other Attendance-related and Performance-related
methods to load and save it, but these methods are not shown in the diagram above.
All Event and StudentList objects are saved after receiving Bye command.
If the program crashes (due to unhandled Exception or Interrupt), they will not
be saved.
3. Implementation of Features
3.1 Event
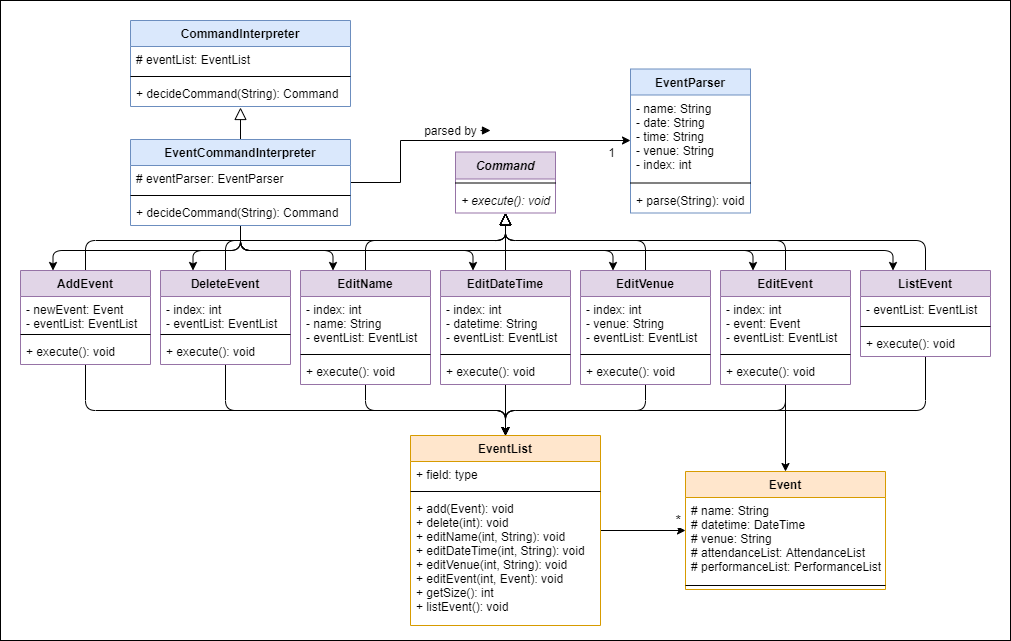
Class diagram of the Event component
The Event features allow users to update and keep track of their schedules.
Program flow
- When a user enters an event-related command, the command is analysed by
EventCommandInterpreter. - The first word is extracted by
getFirstWordto determine thecommandType. - If this
commandTyperequires further arguments, subsequent words are extracted, and parsed byEventParserto retrieve the relevant information (e.g. index, name, time, date, venue). - Alternate paths are chosen based on
commandType, where a correspondingCommandclass is created, with the information extracted from the previous step passed into it.- e.g. Command
event delete i/1will create aDeleteEventobject, withindex=1as its argument.
- e.g. Command
- This command is returned to
CommandInterpreter#decideCommand()which returns toPac#run()to callCommand#execute().
The diagram below illustrates the program flow stated above, with the command
event delete i/1.
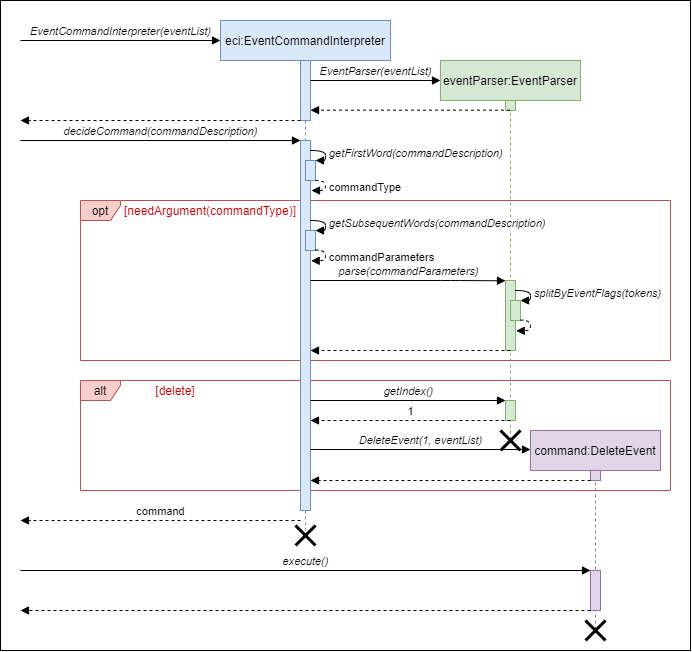
In this diagram:
- Other alternative paths are not shown (e.g. [add], [editEvent], [list], etc.).
- The details after
Command#execute()is not shown.
Note that:
datetimeis stored as a single attribute inEventclass, but it is exposed to user asdateandtime, which corresponds tod/andt/flag respectively.editDateoreditTimecommands are not available. OnlyeditDateTimeis available to change thedateand/ortimeof anEventobject.delete(Event)method is currently not in use, but can be used to implement delete by event name, either by complete match, or fuzzy match.- Any classes (e.g.
Seminar) that inherit fromEventclass will have similar program flow.
3.2 Calendar
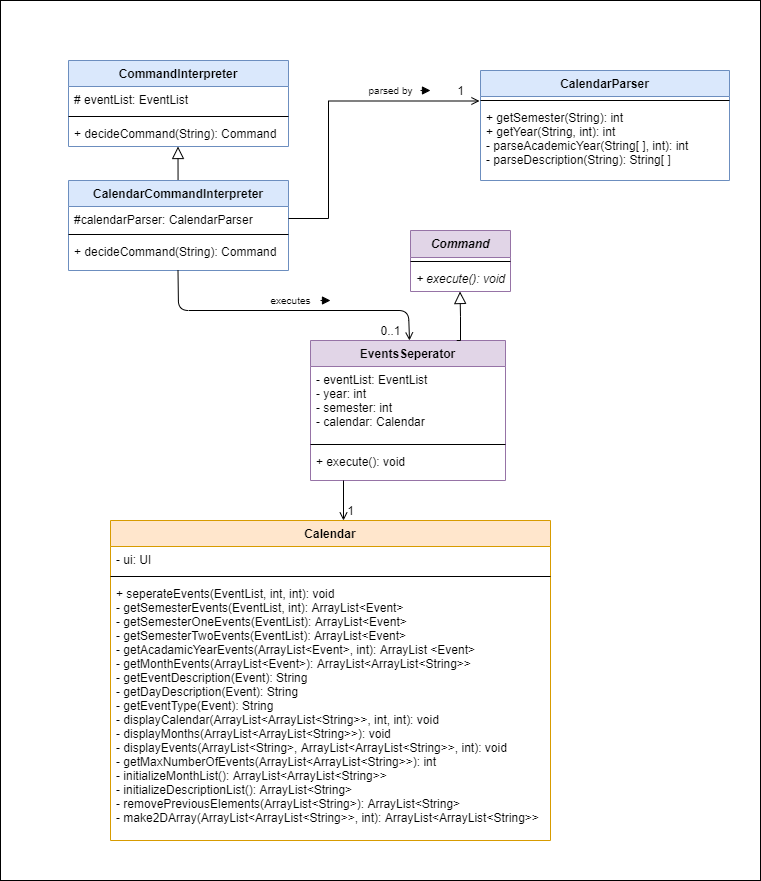
Class diagram of the Calendar component
The calendar feature allows users to view their schedule by semester and academic year. Since our target user is professor, this feature allows the professor to manage their events in accordance to their work schedule.
Calendar Command Interpreter
Below shows the sequence diagram of CalendarCommandInterpreter:
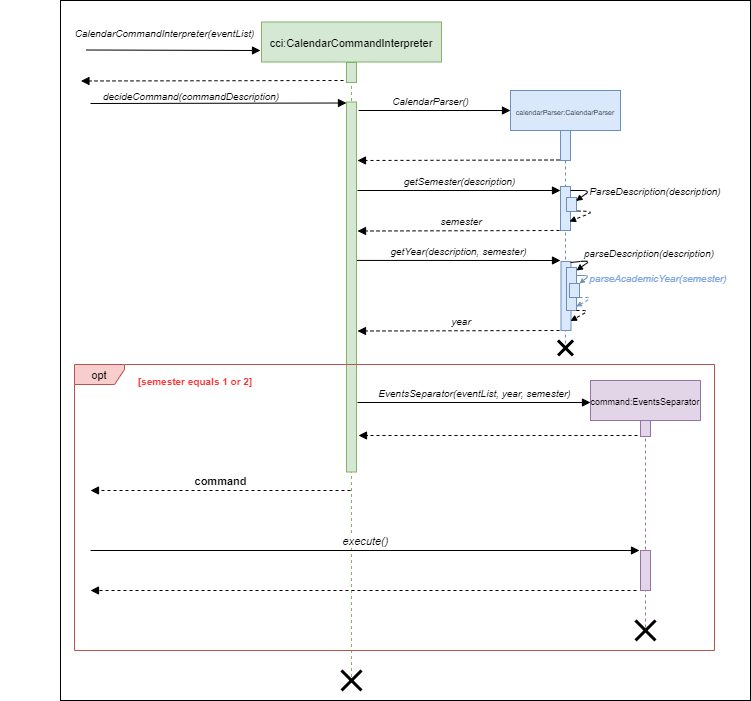
Diagram of CalendarCommandInterpreter
- When a user enters a calendar-related command, the command is analysed by
CalendarCommandInterpreter. - Once determined, the relevant information (eg. semester, academic year) are extracted by
CalendarParser. - Then, only if semester equals 1 or 2 (i.e. valid number), an
EventsSeperatorobject which extendsCommandis created. - This command is then returned
CalendarCommandInterpreter#decideCommandwhich returns toPac#runto callCommand#execute. - If the command is invalid, the interpreter throws PacException to inform the user.
Program flow
- When the user enters the calendar-related command, the command is analysed by CalendarCommandInterpreter and executed as shows in the section above.
command#executewill execute the command and create acalendarobject.uiobject anddisplaytableobject is created in the constructor of the Calendar class.separateEvents()method inCalendarexecutes getSemesterEvents(), getAcademicYearEvents(), and getMonthEvents() to sieve the events that fall under a specific time-frame mentioned by the user.- displayCalendar() method in separateEvents(), displays all the components of the calendar by interacting with the UI and DisplayTable classes.
The diagram below illustrates the program flow stated above:
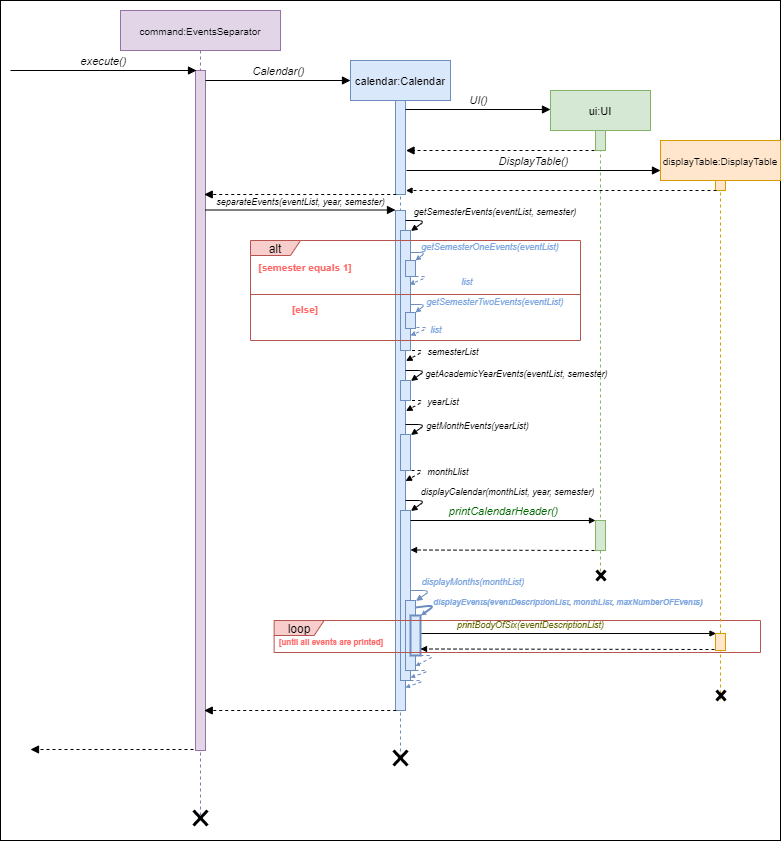
Program flow of calendar execution
Below is an example usage of how the user can interact with the calendar manager:
Step 1: The user wants to add an event to their calendar. They do so by inputting event add n/football d/2020-05-04 t/1700.
Assuming that it is currently semester 2 of the academic year 19-20, this event falls in that timeline and is added to the calendar.
Step 2: The user realises that the name of the event is wrong and decides to edit the name of the event. First, they input
event list to find the index of the event. Assuming the index of the event is 4, the user then inputs event editname i/4 n/frisbee
to edit the name of the event.
Step 3: The user wants to display the events that fall under semester 2 of academic year 19-20. To do this, the user inputs
calendar s/2 ay/19-20. A sample view of the calendar is shown below:
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
SEMESTER 2 AY 19/20
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
| JAN | FEB | MAR | APR | MAY | JUN |
|_____________________|_____________________|_____________________|_____________________|_____________________|_____________________|
| | | | | 4th [E]: frisbee | |
|_____________________|_____________________|_____________________|_____________________|_____________________|_____________________|
Design considerations
Aspect: Data Structure used to implement calendar
- Alternative 1: Save the events using both 1D ArrayList and 2D ArrayList.
- Pros: Allows flexibility as to what information a calendar can store. For example, the 1D ArrayList is used to store the event descriptions as Strings whereas the 2D ArrayList stores events which corresponds to each month.
- Cons: Poor performance when retrieving events which fall within a certain time-frame as program needs to iterate through multiple ArrayLists.
- Alternative 2: Save the events as a sorted tree map
- Pros: Able to utilise existing java interface to implement calendar instead of creating new object.
- Cons: Poor performance when user makes changes to event list to calendar as tree map needs to perform sorting for every new addition, deletion or editing.
Aspect: How addition, deletion and editing of events affects calendar execution
- Alternative 1(current choice): Implement a class specifically to interact with the calendar
- Pros: Calendar class can support different interactions to modify calendar content
- Cons: Many new methods to be implemented, which affects code readability.
- Alternative 2: Modify calendar directly using methods belonging to a class where it can be stored in
- Pros: Does not require instantiation of new object to modify the calendar contents.
- Cons: Many new methods to be implemented, which affects code readability.
Note that:
- Event list should contain existing events with date and time to view the calendar.
- Input of the both academic years should be double digit, e.g ay/07-08, ay/19-20.
acadamic yearis parsed inCalendarParserand only one year is returned toCalendarCommandInterpreteraccording to the semester input by the user, i.e s/1 ay/19-20 would return year = 19, s/2 ay/19-20 would return year = 20.- Calendar view of the whole year is not available. Only semester 1 or 2 of an academic year can be viewed at a time. This is due to the optimization of calendar view in accordance to the professor’s schedule.
- Event name size must be less than 10 characters to be displayed neatly (current implementation), however it can be implemented in the future to truncate longer names to fit nicely in the calendar.
- Addition, deletion and editing of events from the calendar are automatically attempted whenever a user enters a
command to modify an event from the event list.
This is illustrated in the flowchart below:
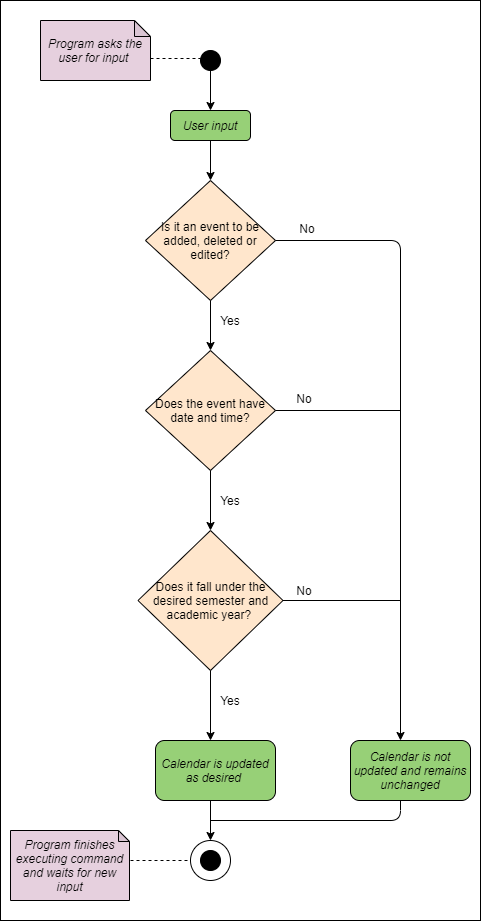
Calendar management activity diagram
3.3 Attendance
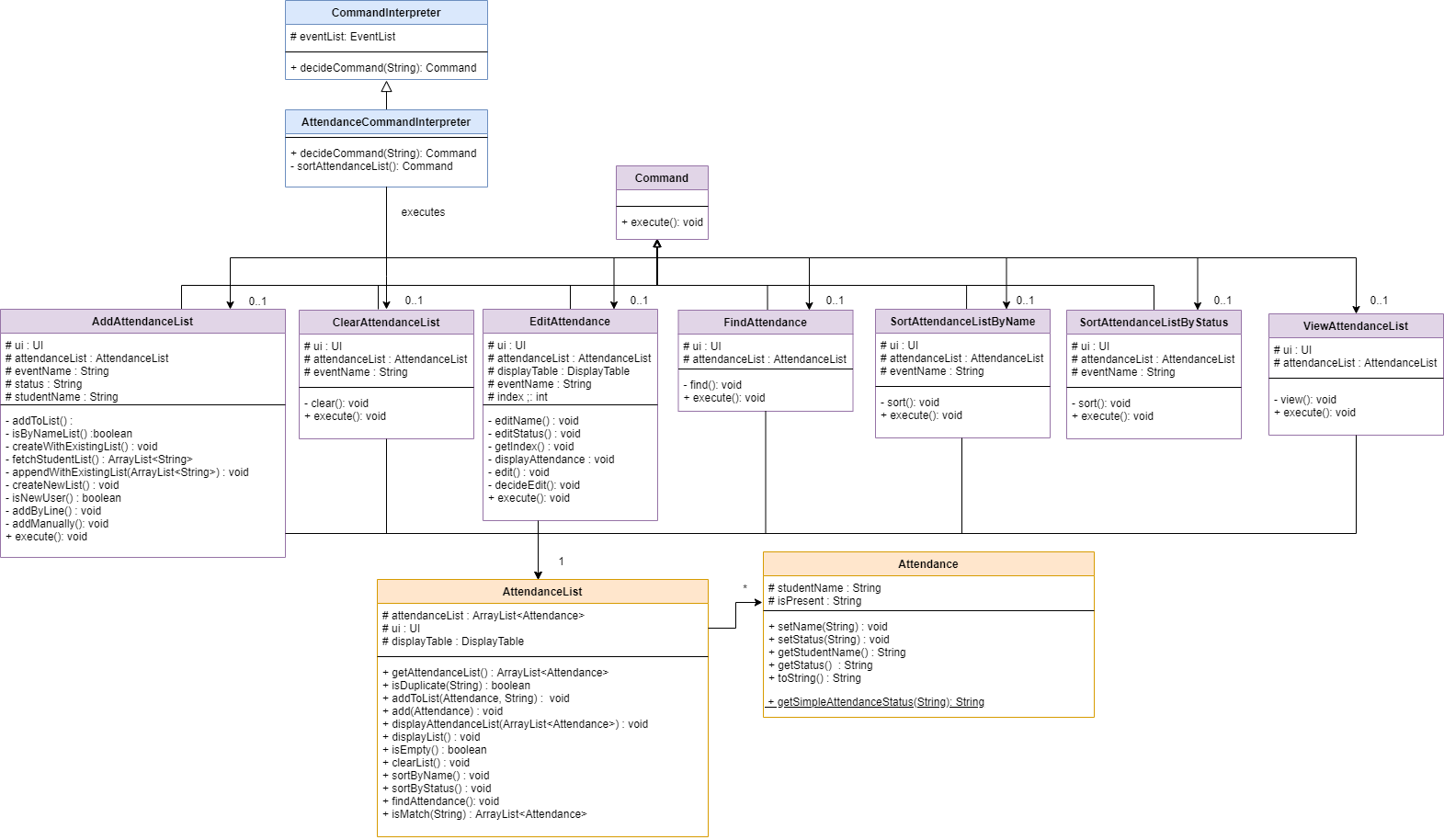
Class diagram of the Attendance component
The Attendance features allow users to update and keep track of their students’ attendance for a Event.
Attendance Command Interpreter
Attendance Command Interpreter interprets the user input when it belongs to the attendance category. When user input is passed to Attendance Command Interpreter, it extracts the second word in the user input and decides whether the string can be interpreted as a valid Command. If valid, the interpreter returns its corresponding Command. Else, the interpreter will throw PacException to inform the user that the string is interpreted as an invalid Command. Below shows the flow chart and sequence diagram of Attendance Command Interpreter.
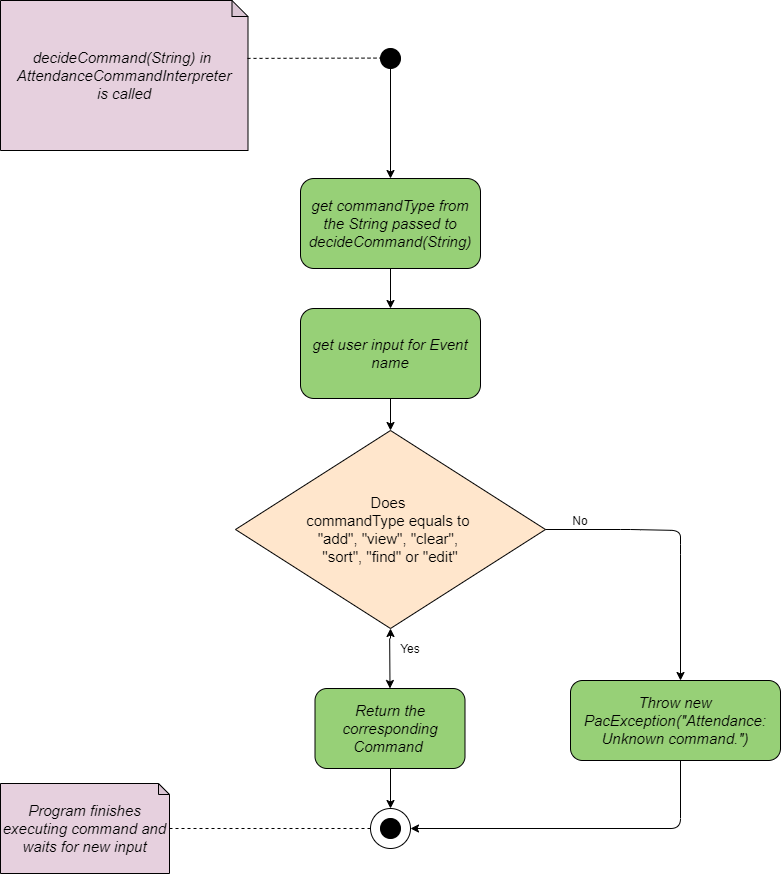
Flow Chart of Attendance Command Interpreter
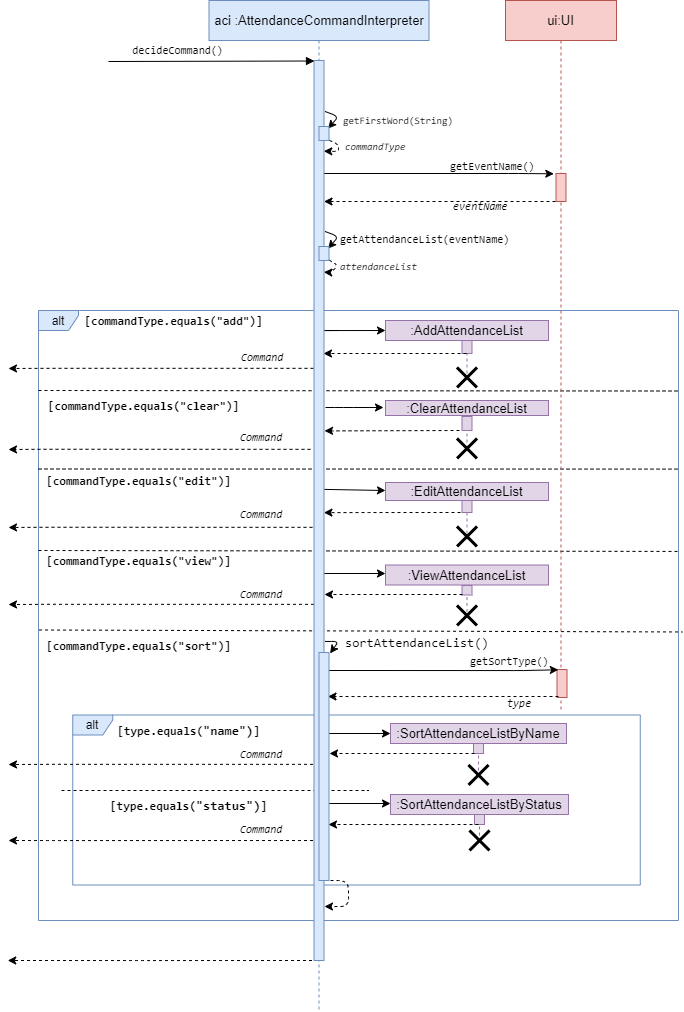
Sequence diagram of Attendance Command Interpreter
Program flow
- When a user enters an attendance-related command, the command is analysed by
AttendanceCommandInterpreter. - Once determined, the relevant class that corresponds to the type of command is created.
- Then, the class will execute base on its function. It modifies
AttendanceList. - These commands are then returned to
Pac.run()toexecute().
Note that:
attendance addcommand provides to use an existing list stored underStudentListCollectionor to create a new list. If you choose to use an existing list, you need to ensure that there are existingStudentListin theStudentListCollection. If you choose to create a new list, you will be given an option of a multi-line or single line interaction. If you are a new user, you will be assigned to use the multi-line entering of student attendance data. If you are not a new user, you will assigned to use the single line entering of student attendance data.n/andp/flags are used to insert new attendance.
Features under Attendance
There are 6 features for attendance in total, as shown below. The features will be presented in the order of sequence diagram, followed by description.
Add attendanceList
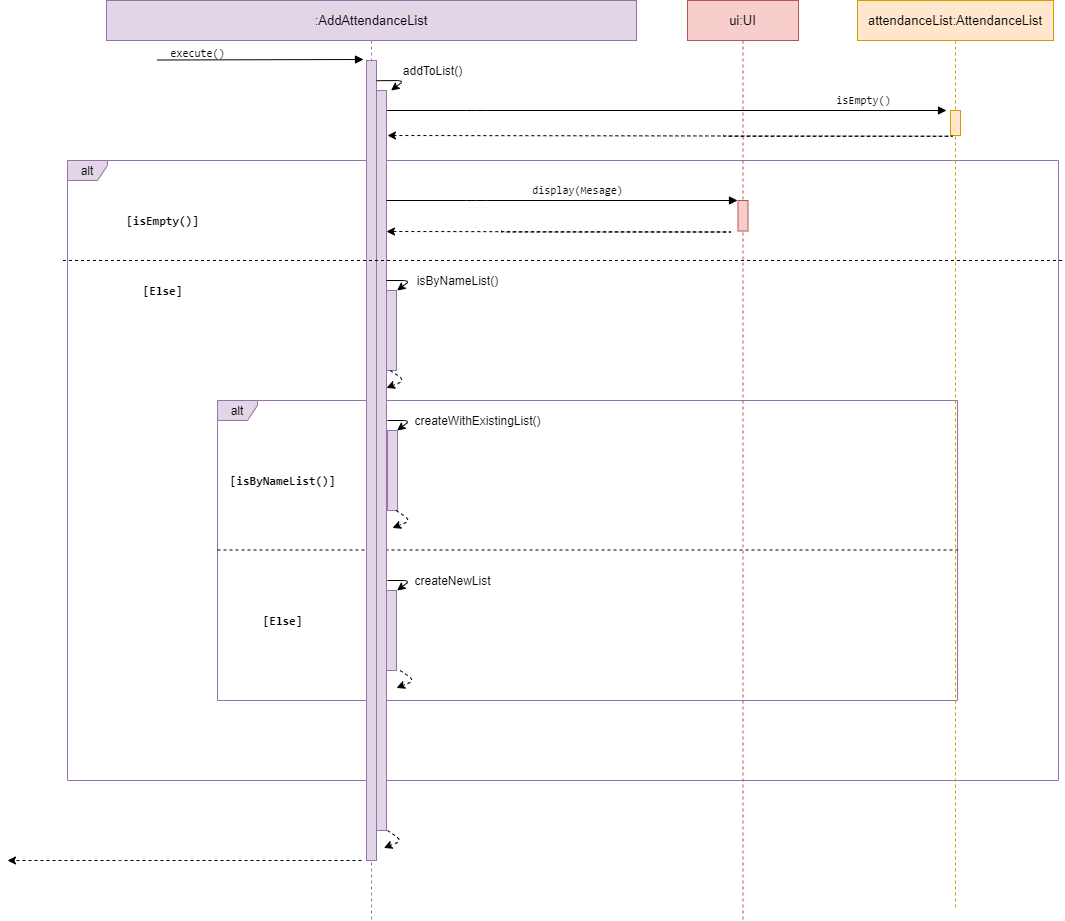
Sequence diagram of AddAttendanceList
AddAttendanceList is a subclass of Command. It allows the user to add a new existing attendanceList under an Event.
The method addToList() accesses the attendanceList of a given event, and checks whether the list is empty. If there is
an existing attendanceList in the given event, it calls display() in UI and inform the user that the list currently
exist and needs to be cleared before adding a new attendanceList. Else, it will prompt the user to ask whether the
user intends to use an existing studentList found in studentListCollection or create a new list which will be added
to studentListCollection upon creation with the name of the event as the list name.
Clear attendanceList
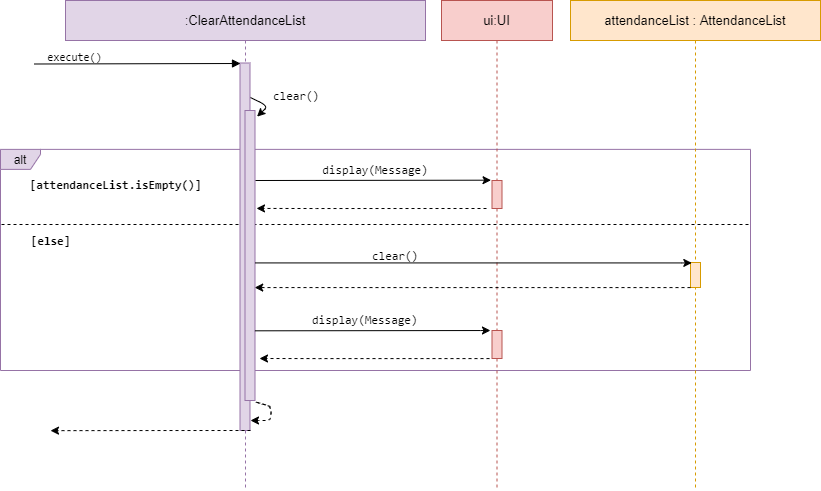
Sequence diagram of ClearAttendanceList
ClearAttendanceList is a subclass of Command. It allows the user to clear an existing attendanceList under an Event.
The method clear() accesses the desired attendanceList of a given event, and checks whether the list is empty.
If empty, it calls display() in UI and inform the user list is empty. Else, it will clear the existing attendanceList
stored under the given event.
View attendanceList
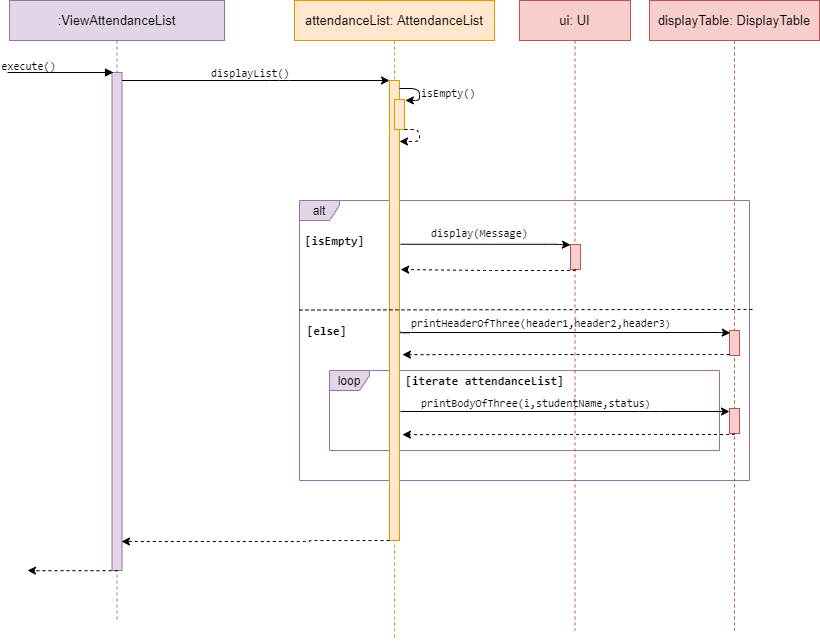
Sequence diagram of ViewAttendanceList
ViewAttendanceList is a subclass of Command. It allows the user to view a self generated table based on the data
in a desired attendanceList.
The method view() accesses the desired attendanceList of given event, and checks whether the list is empty.
If empty, it calls display() in UI and inform the user list is empty. Else, it will iterate through the attendanceList
and print Attendance data in a table format.
Sort attendanceList
-
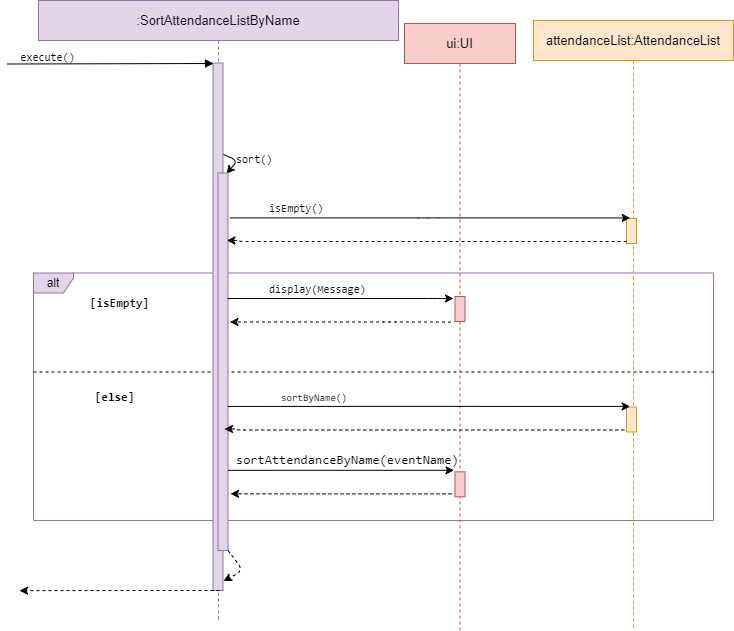
Sequence diagram of SortAttendanceListByName
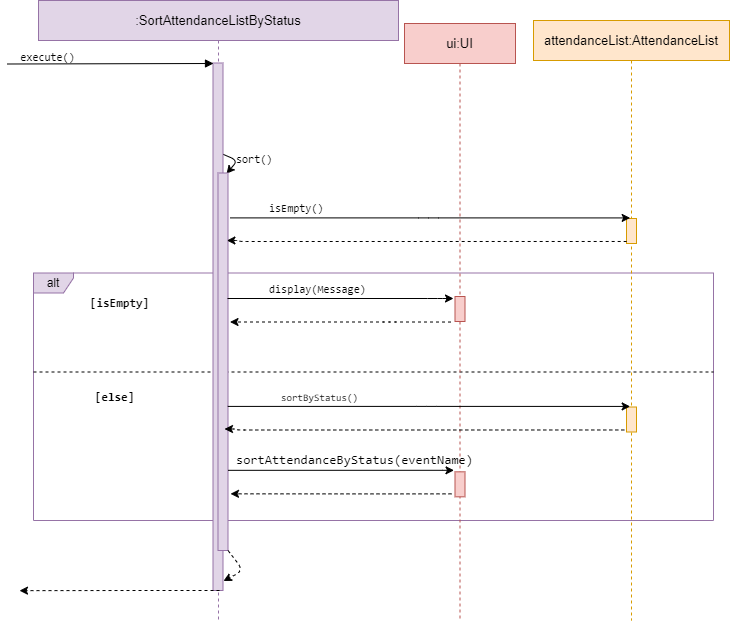
Sequence diagram of SortAttendanceListByStatus
SortAttendanceListByName and SortAttendanceListByStatus are subclasses of Command.
They both allow the user to sort a attendance list by either the student’s name or status.
The two Commands will be discussed together in this section as they have similar behaviour.
The methods SortAttendanceListByName and SortAttendanceListByStatus access a desired attendanceList and check
whether it is empty. If empty, it calls display() in UI and inform the user list is empty.
Else, it will sort the attendanceList by the type mentioned in its method name.
Edit attendance
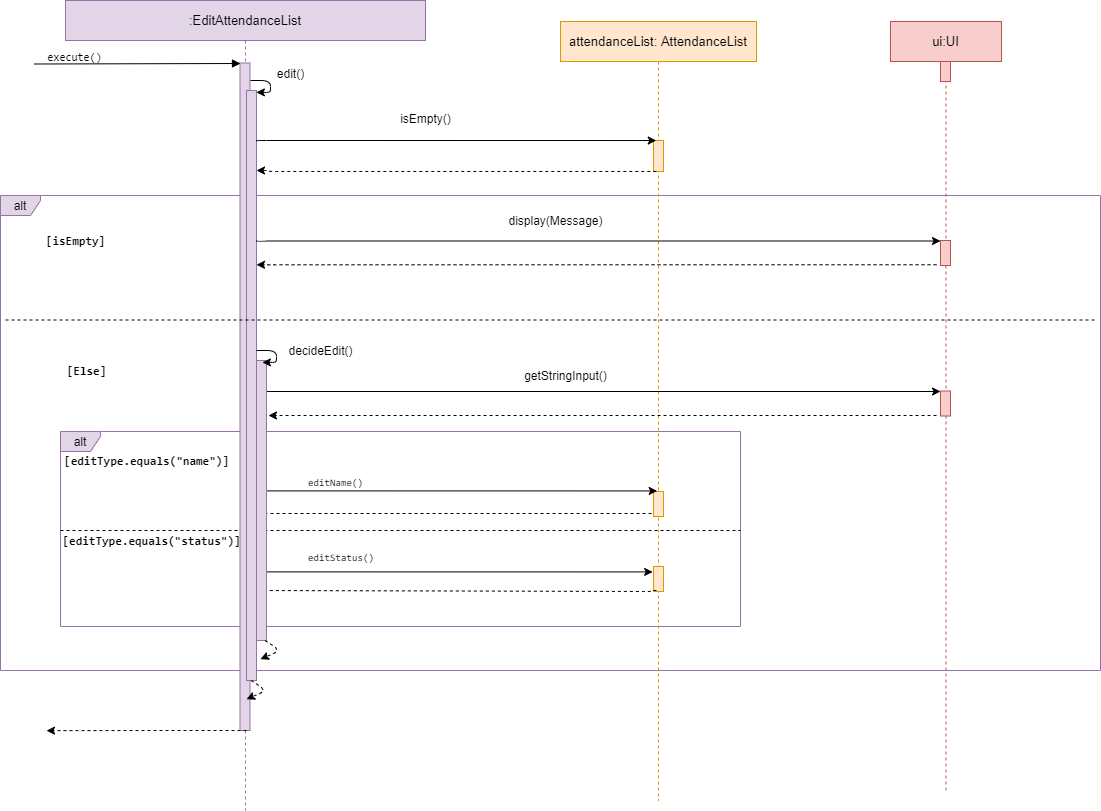
Sequence diagram of EditAttendance
EditAttendance is a subclass of Command. It allows the user to edit an attendance,
either the student’s name or status, from a desired attendanceList under an Event.
The method edit() accesses the desired attendanceList of given event, and checks whether the list is empty.
If empty, it calls display() in UI and inform the user list is empty. Else, it will call decideEdit() from itself.
The method decideEdit() will call getUserInput() in UI to get the user input and decide whether to call editName() or
editStatus() base on the user input.
Find attendance
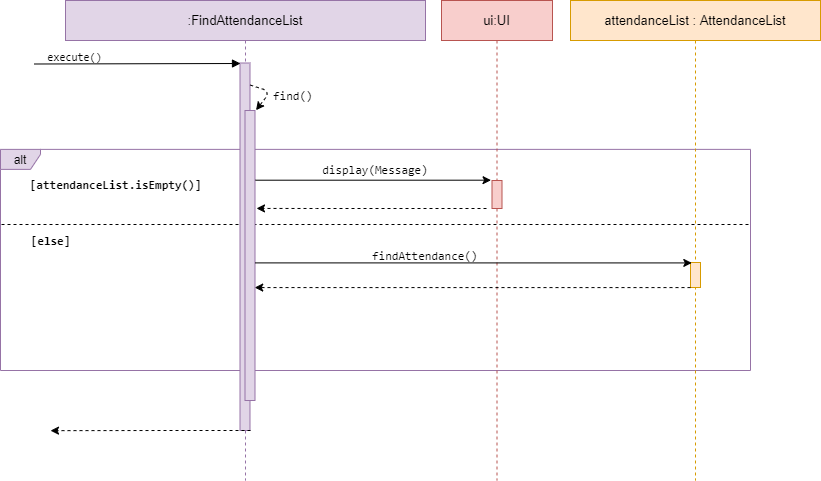
Sequence diagram of FindAttendance
FindAttendance is a subclass of Command. It allows the user to find an attendance.
The method find() accesses the desired attendanceList of given event, and checks whether the list is empty.
If empty, it calls display() in UI and inform the user list is empty. Else, it will call findAttendance() from
attendanceList. findAttendance() will search for attendance with the same name entered and display for the user.
Design consideration for Attendance
AddAttendance
- Alternative 1 : Use single line for adding of attendance to an event
- Pros: Prompts the user what to type
- Cons: Slow for experience users
- Alternative 2 : Use multi-line for adding of attendance to an event
Using single line or multi-line for adding of attendance to an event
- Pros: Fast for experience users
- Cons: New users will have difficulty in adding new attendance
- Final Decision : Using both single line and multi-line by giving the user the option
ClearAttendance VS DeleteAttendance
- Alternative 1 : Allow the deletion of a single attendance in an attendance list in an event
- Pros User can specifically remove a single student
- Cons Complicated feature to use as user will need to search for the attendance in the list before deletion
- Alternative 2 : Only allow the attendance list to be cleared
- Pros User can easily remove the attendance list and add a new attendance list
- Cons A single mistake in the attendance list will mean that user has to clear and add again.
- Final Decision: Introduce a feature to
editAttendanceto amend mistake and haveclearAttendanceinstead ofdeleteAttendance.deleteAttendancecan be inserted in future releases.
3.4 Performance
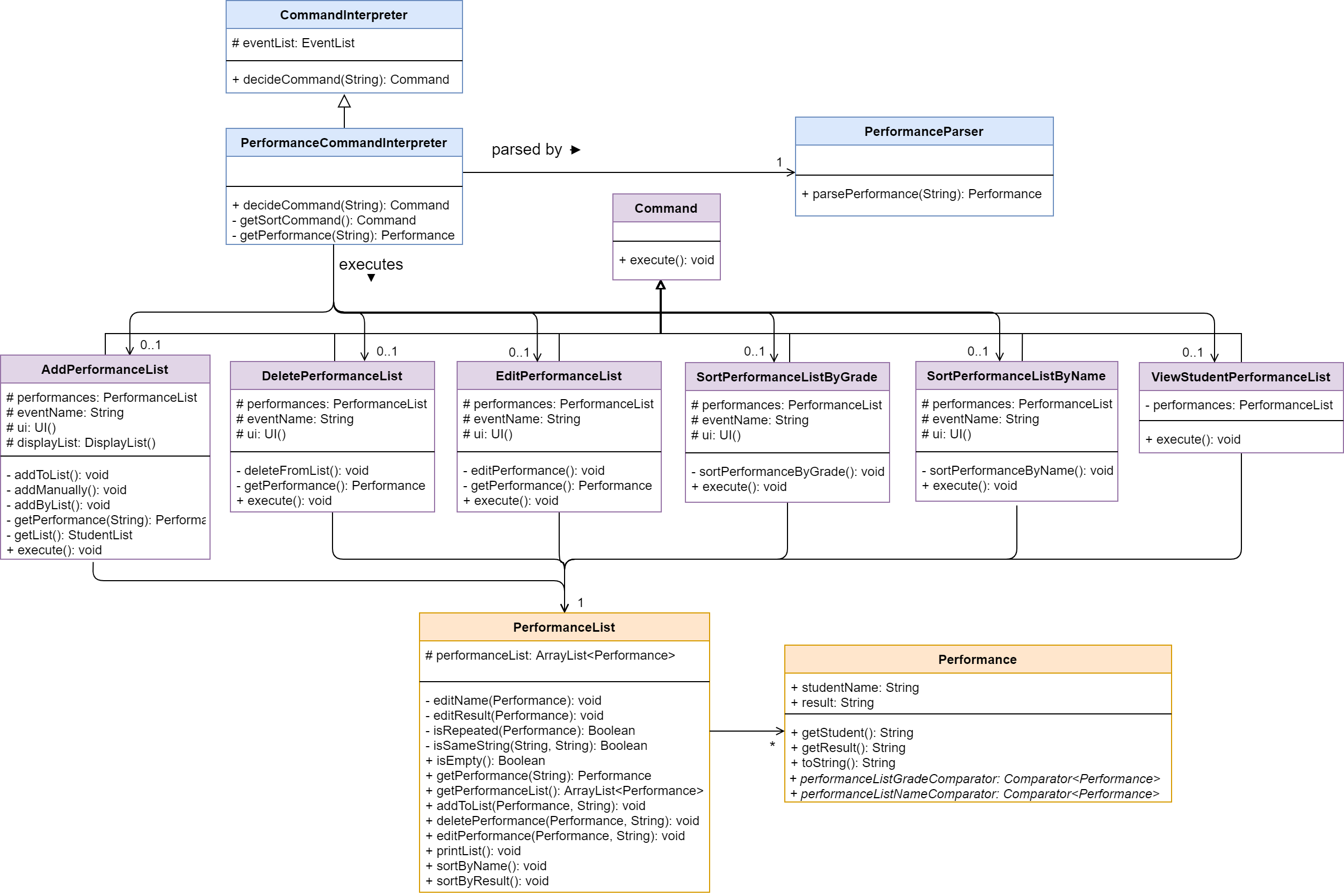 Class diagram of the Performance component
Class diagram of the Performance component
The Performance features allow users to update and keep track of their students’ result for a Event.
Performance Command Interpreter
Performance Command Interpreter interprets the user input when it belongs to the
performance category.
When user input is passed to Performance Command Interpreter, it extracts the
second word in the user input and decides whether that string can be interpreted to a
valid Command.
If valid, the interpreter returns its corresponding Command.
If invalid, the interpreter throws PacException to inform the user.
Below shows the flow chart and sequence diagram of Performance Command Interpreter.
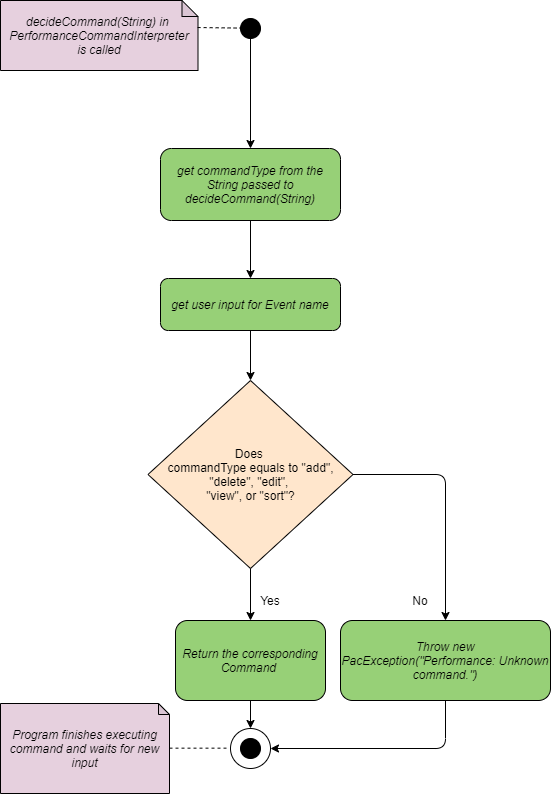
Flow Chart of Performance Command Interpreter
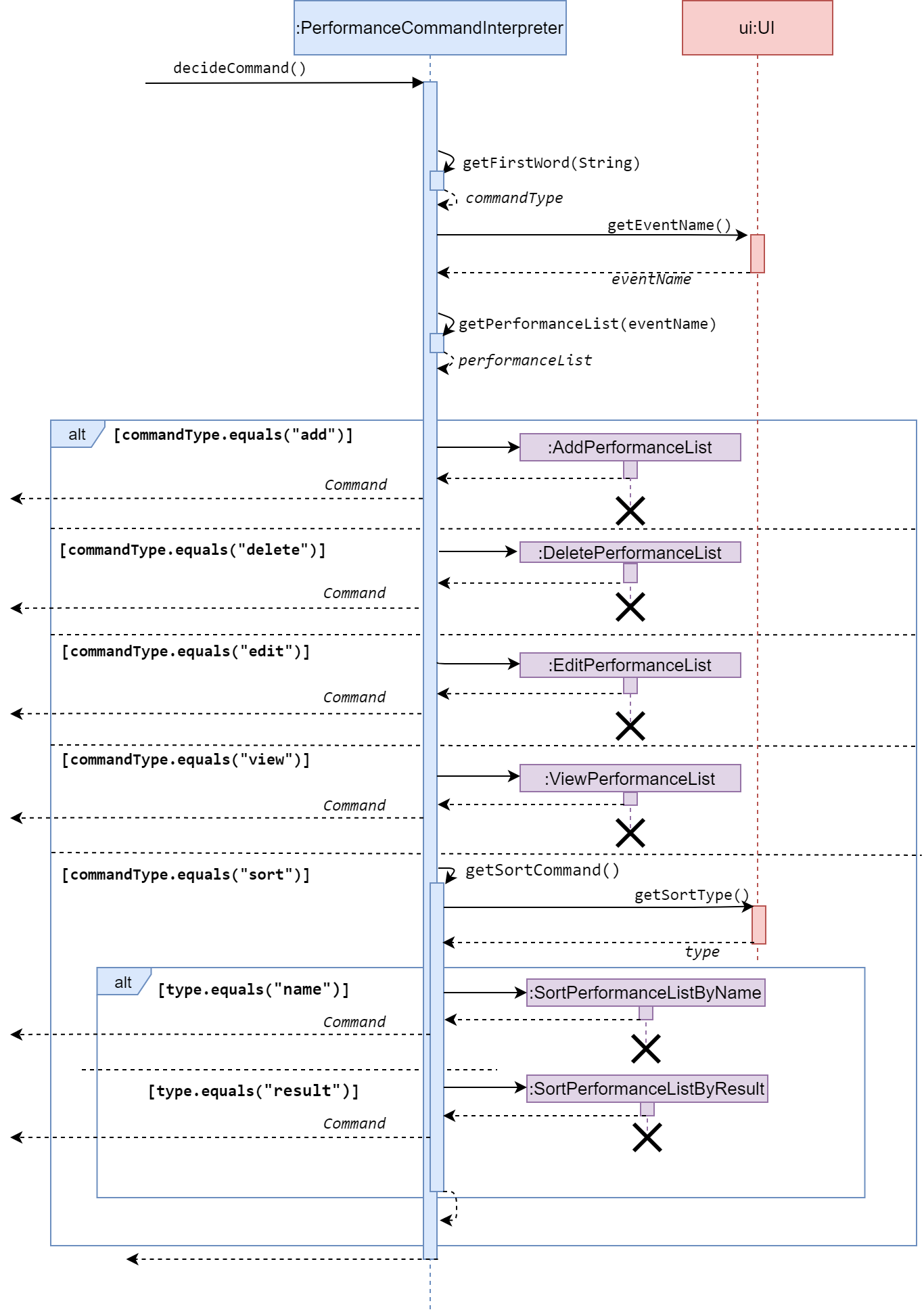 Sequence diagram of Performance Command Interpreter
Sequence diagram of Performance Command Interpreter
Program flow
- When a user enters a performance-related command, the command is analysed by PerformanceCommandInterpreter.
- Once determined, the relevant class that corresponds to the command is created (e.g. AddPerformance, DeletePerformance…), and ask for relevant information (e.g. event name, student name, student result) from the user.
- Then, with the information extracted from the previous step passed into it. It modifies PerformanceList` under the event class correspond to the input event name.
- These commands are then returned to
Pac.run()toexecute().
Note that:
- All PerformanceList class are created under an Event. A PerformanceList cannot exist by its own.
- All Performance commands are step-by-step commands. This aims to provide convenience to the user by prompting instructions and correct command format.
- All Performance discussed in Pac are constructed with student’s name and result.
Features under Performance
There are 5 features for Performance in total, as shown below. The features will be presented in the order of sequence diagram, followed by description.
Add performanceList
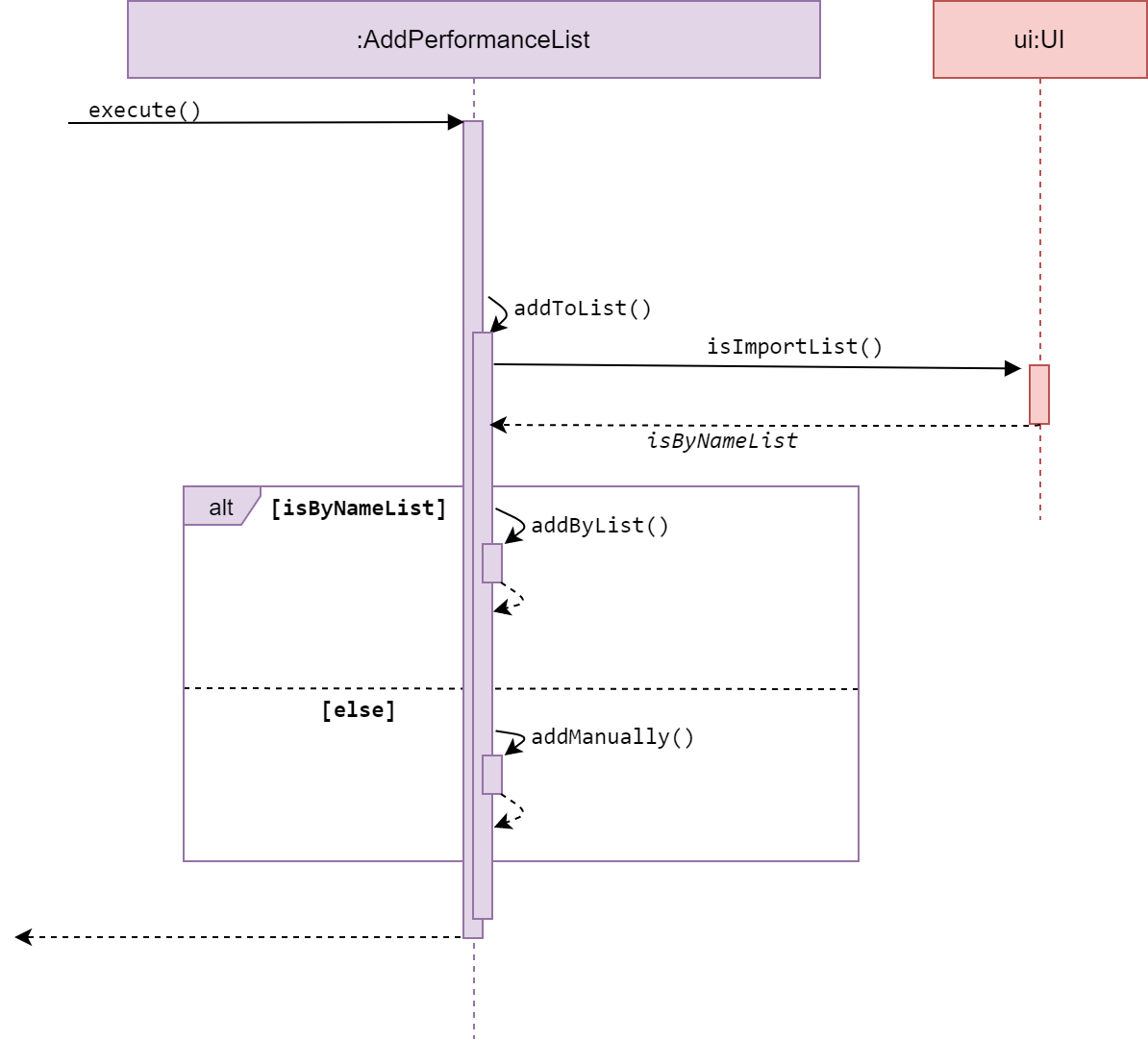
Sequence diagram of AddPerformanceList
AddPerformanceList is a subclass of Command. It allows the user to add performances by importing a student list, or add manually, to a desired performance list under an Event.
The method execute() calls addToList() from the same class, which then calls
isImportList() from UI to get a user input. This user input decides whether
the user will add performances by list or manually.
The method addByList() or addManually() will then get user input for Performance parameters,
which will be parsed by the PerformanceParser and return a Performance.
The Performance attained from the parser will be added to a desired performanceList.
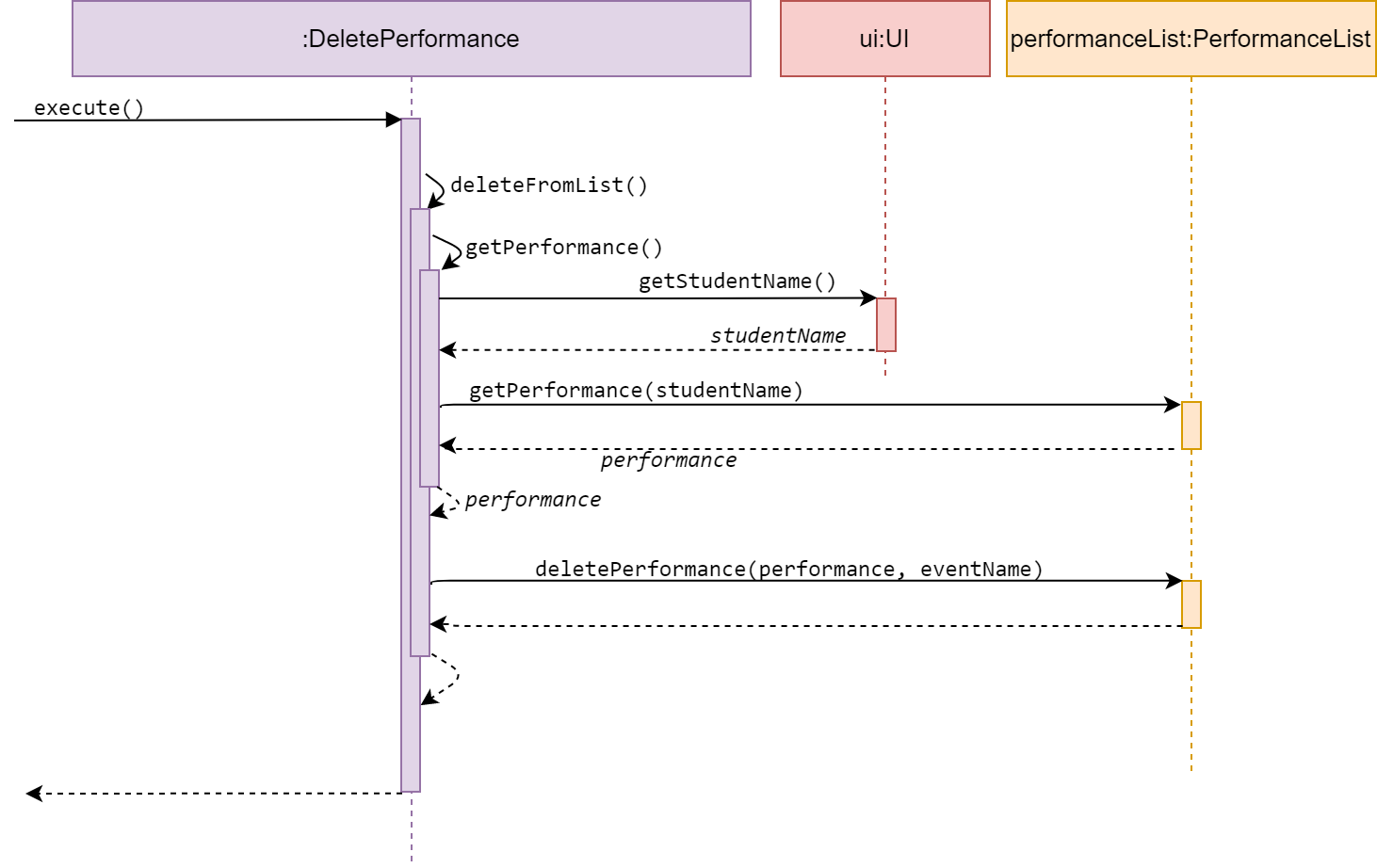
Delete performanceList
Sequence diagram of AddPerformance
DeletePerformanceList is a subclass of Command. It allows the user to delete a performance from a desired performance list under an Event.
The method execute() calls deletePerformance() from the same class, which then calls
getPerformance() from itself to get the user input, Performance parameters
of the Performance to be deleted, and return a Performance.
The Performance attained from getPerformance() will be deleted from a desired performanceList.
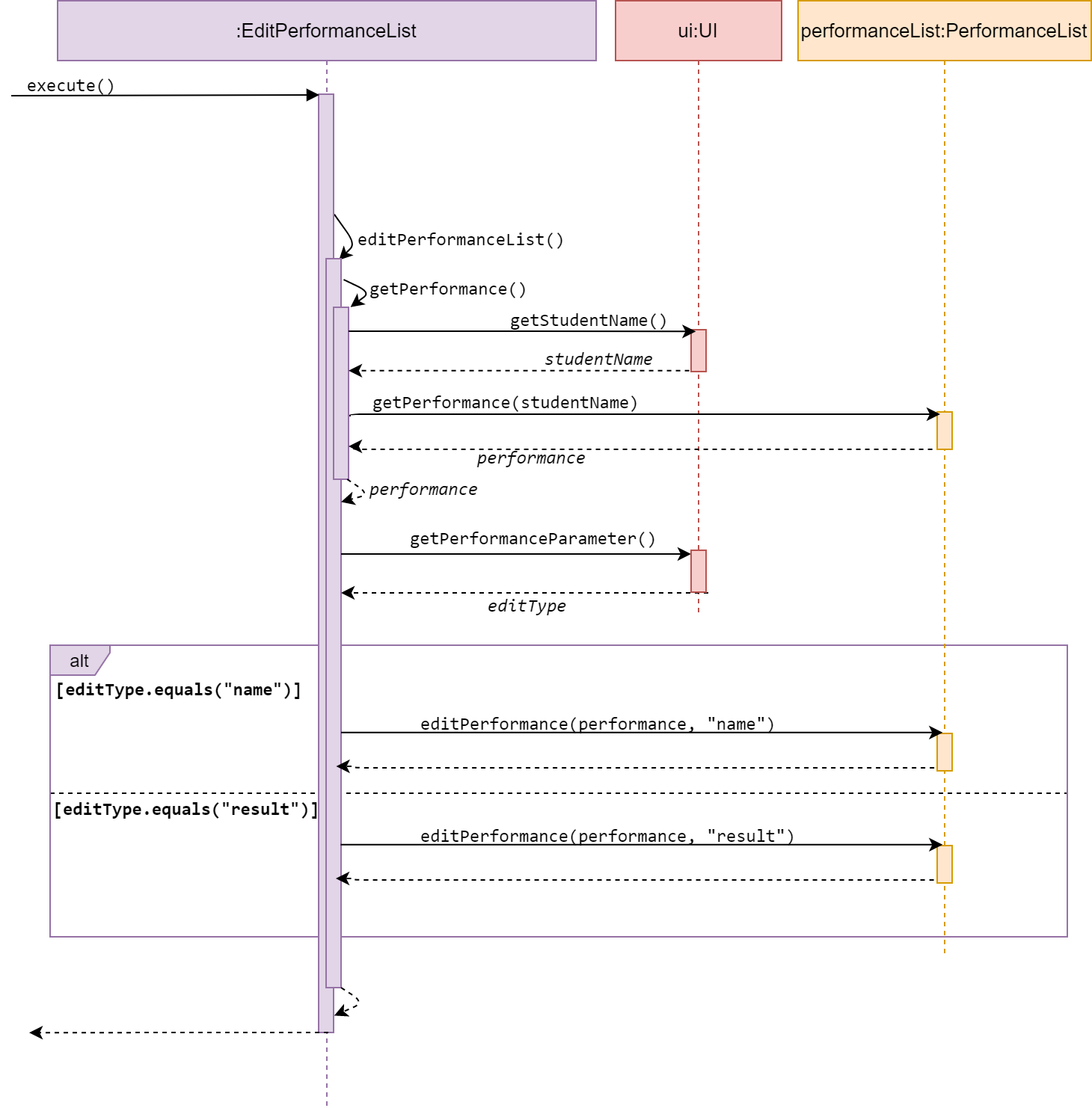
Edit performanceList
Sequence diagram of EditPerformance
EditPerformanceList is a subclass of Command. It allows the user to edit a performance, either the student’s name or result, from a desired performance list under an Event.
The method execute() calls editPerformanceList() from the same class, which then calls
getPerformance() from itself, to get the user input, student’s name of the
Performance to be edited, and return a Performance.
The method editPerformanceList() then calls getPerformanceParameter() from UI
to get a user input. This user input decides whether the user will edit the
student’s name or result.
The new parameter will be attained from the user in method editPerformance(performance, editType)
in PerformanceList.
Sort performanceList
-
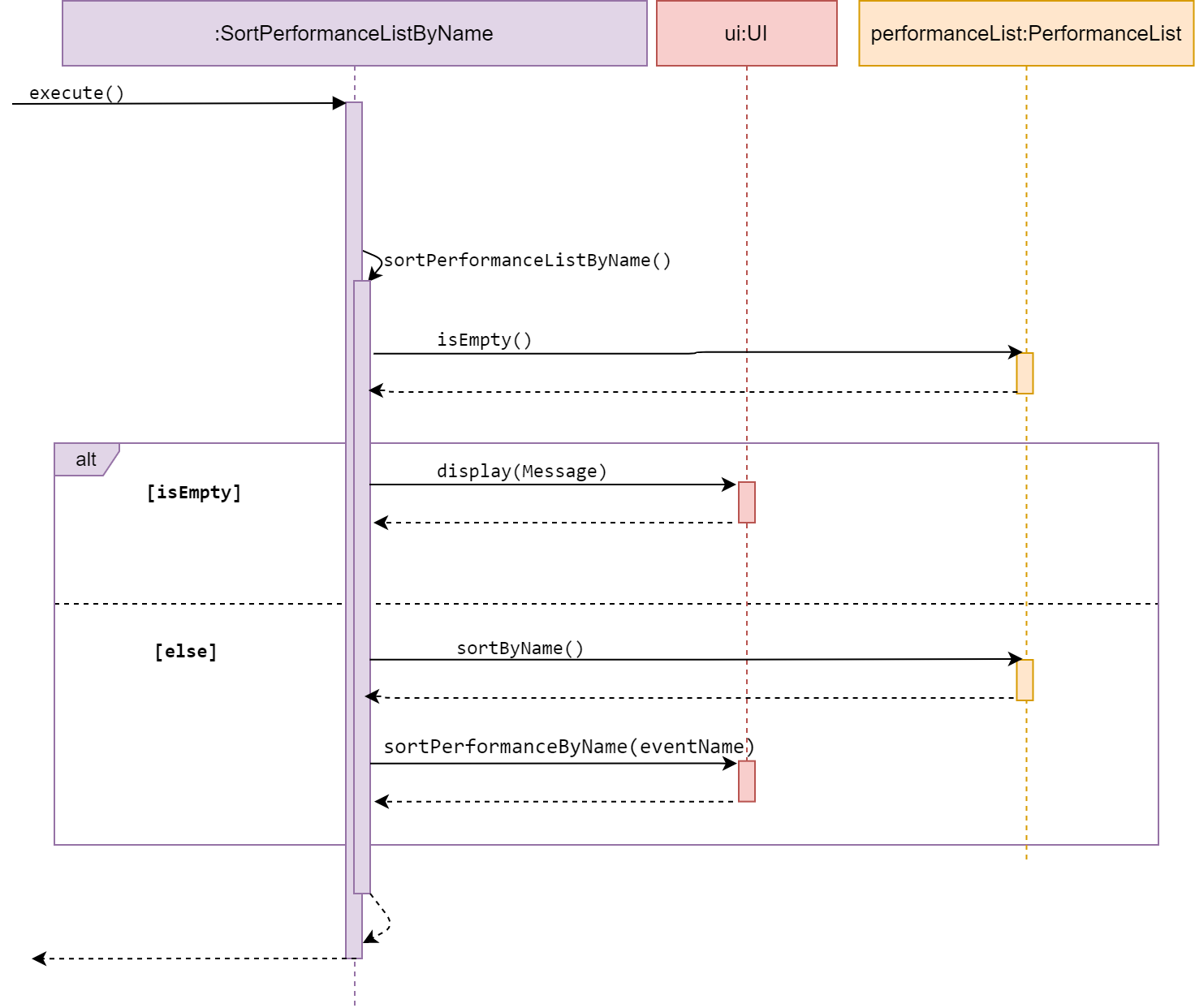
Sequence diagram of SortPerformanceListByName -
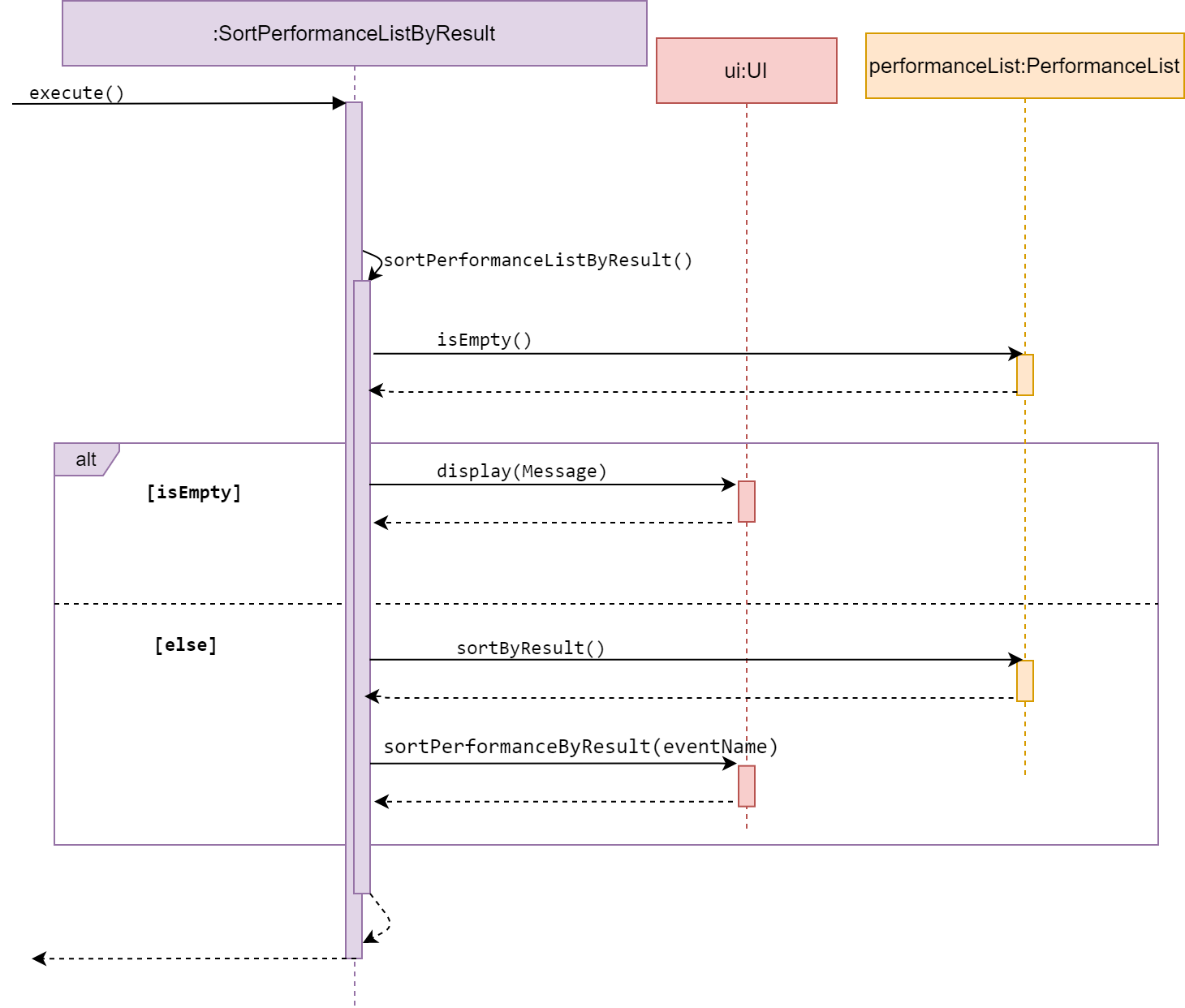
Sequence diagram of SortPerformanceListByResult
SortPerformanceListByName and SortPerformanceListByResult are subclasses of Command.
They both allow the user to sort a performance list, by student’s name or result as their
name suggest.
The two Commands are discussed together in this section as they have similar behaviour.
The method execute() calls sortPerformanceByName() or sortPerformanceByResult,
according to its class name.
The methods sortPerformanceBy…() access a desired performanceList and check whether
the list is empty.
If empty, it calls display() in UI and inform the user.
Else, it will sort the performanceList by the type mentioned in its method name.
View performanceList
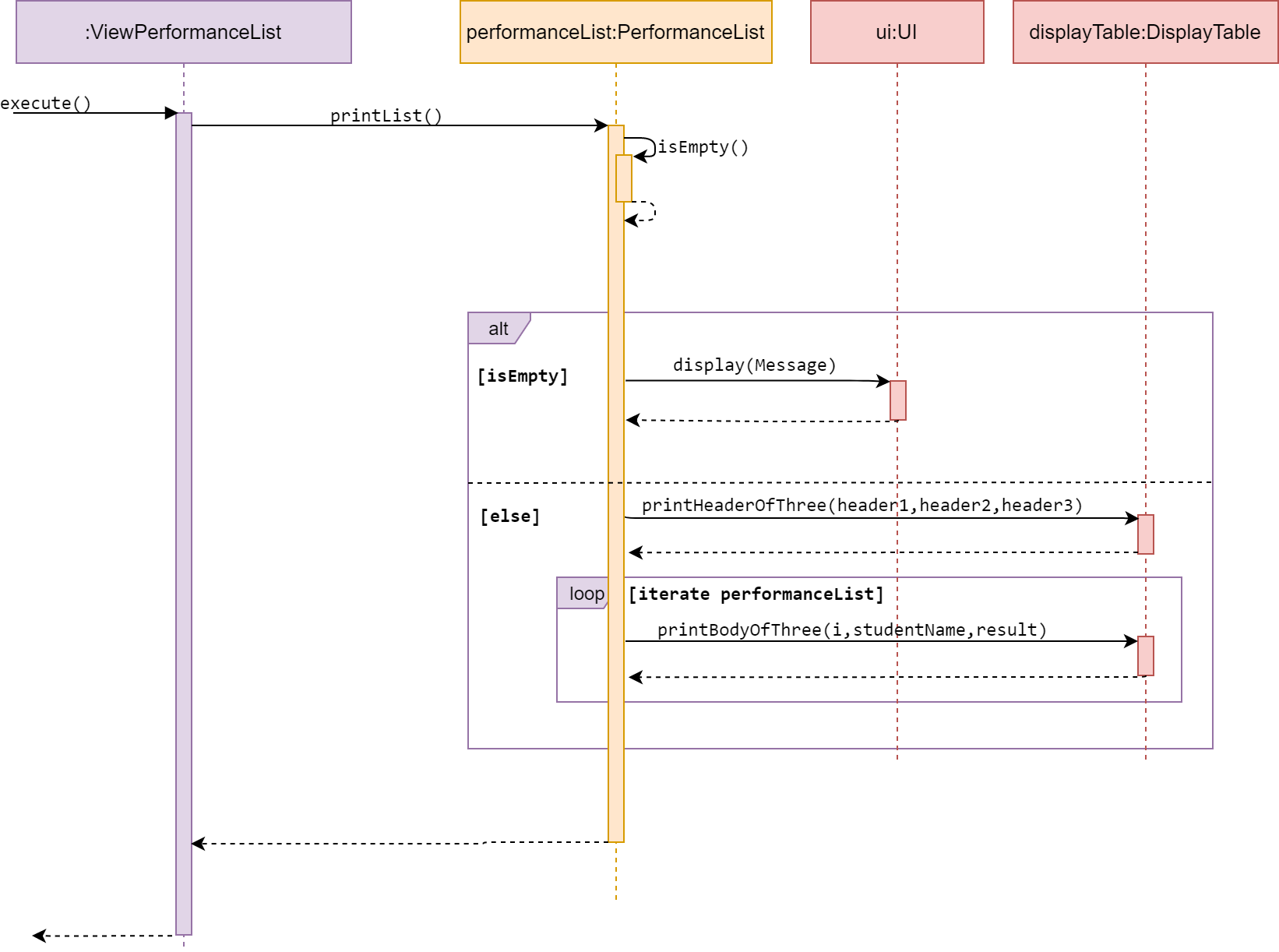
Sequence diagram of ViewPerformanceList
ViewPerformanceList is a subclass of Command. It allows the user to view a self generated table based on the data in a desired performance list.
The method execute() calls viewList() from the same class, which accesses a
desired performanceList of given event and checks whether that list is empty.
If empty, viewList() calls display() in UI and inform the user.
Else, it will iterate through the performanceList and print Performance
data in a table format.
3.5 Student List Collection
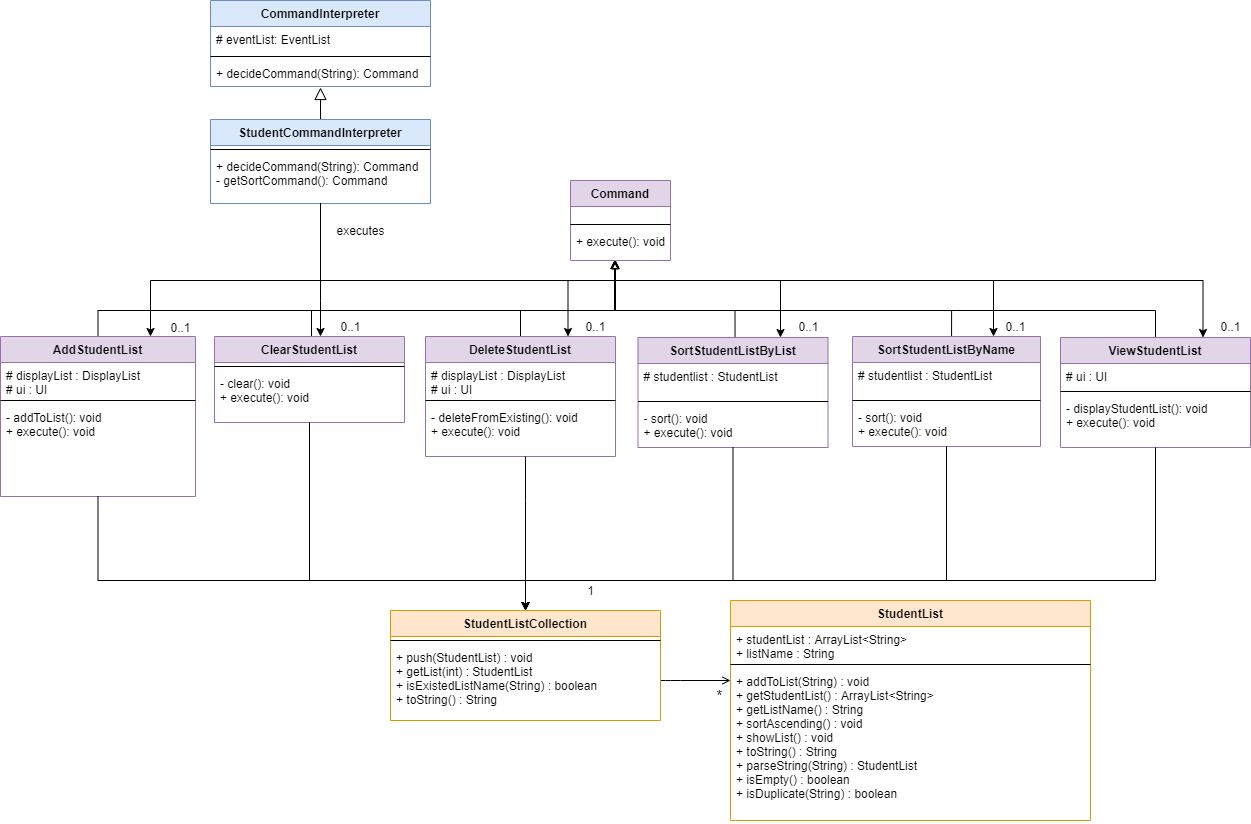
Class diagram of the Student component
The Student list features allow users to store a list of student names, which could be used when updating students’ attendance and performance data conveniently.
Program Flow
- When a user enters an studentList-related command, the command is analysed by
StudentCommandInterpreter. - Once determined, the relevant class that corresponds to the type of command is created.
- Then, the class will execute base on its function. It modifies
StudentList. - These commands are then returned to
Pac.run()toexecute().
Note that:
- studentList-related commands can be executed without the existence of events.
Student Command Interpreter
Student Command Interpreter interprets the user input when it belongs to the
student category.
When user input is passed to Student Command Interpreter, it extracts the second word in the user input
and decides whether that string can be interpreted to a valid Command.
If valid, the interpreter returns its corresponding Command.
If invalid, the interpreter throws PacException to inform the user.
Below shows the flow chart and sequence diagram of Student Command Interpreter.
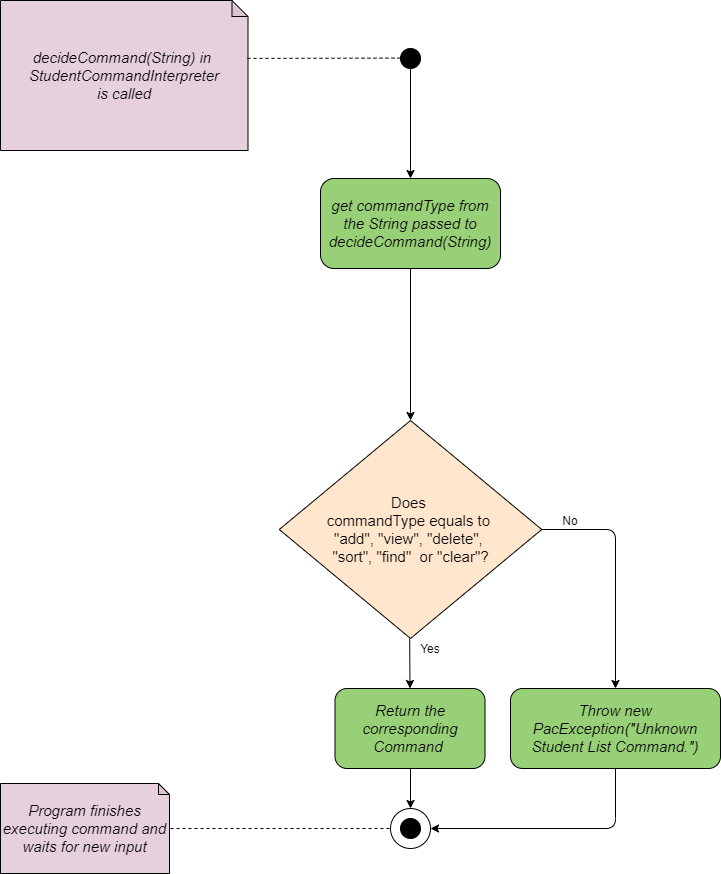
Flow Chart of Student Command Interpreter
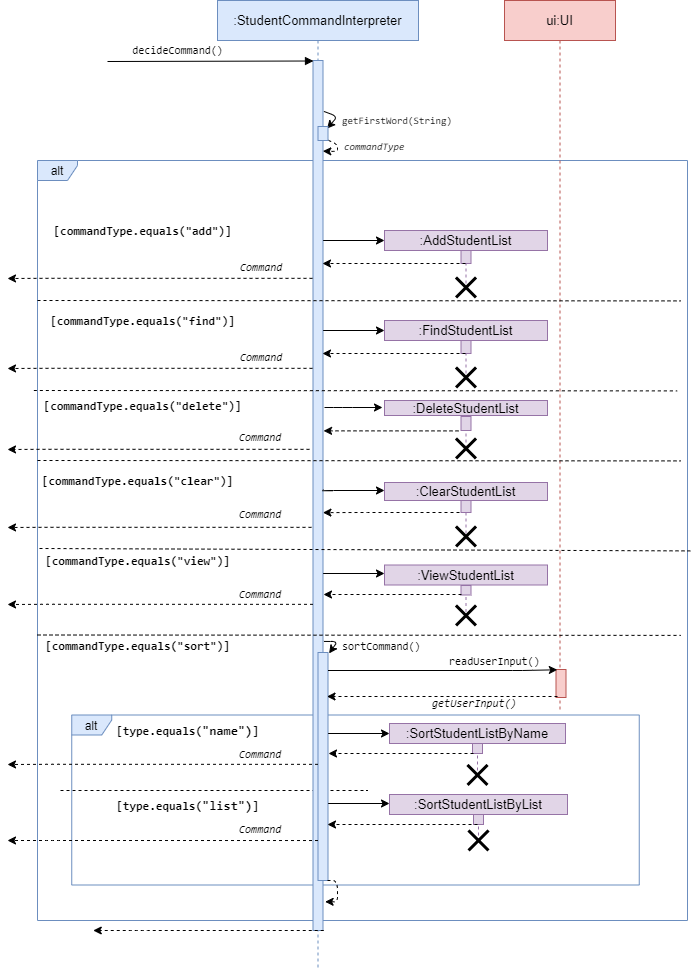
Sequence diagram of Student Command Interpreter
Features under Student List Collection
There are 6 features for Student in total, as shown below. The features will be presented in the order of sequence diagram, followed by description.
Add student list
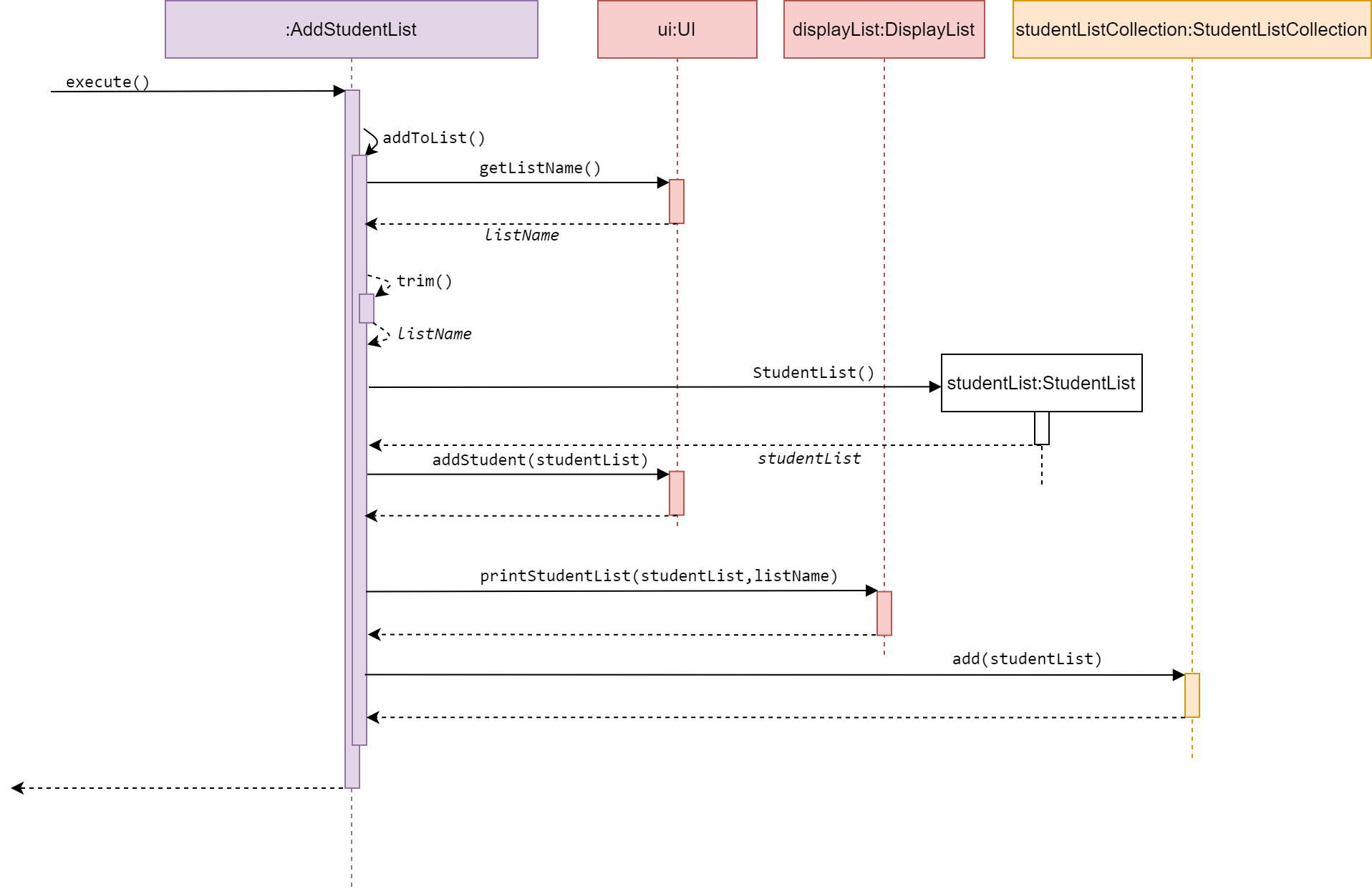
Sequence diagram of AddStudentList
AddStudentList is a subclass of Command. It allows the user to add a student list
to the studentListCollection.
The method execute() calls addToList() from the same class, which then calls
getListName() from UI to get a user input for listName.
The list name of student list is restricted to one word only, hence the parameter listName
is trimmed.
StudentList, a new student list is created with list name listName.
The method addToList() calls addStudent(studentList) from UI to get user input
for student names to be added. The names are added to studentList
in addStudent(studentList).
After user has done input, studentList will be printed, and this new list is
added to studentListCollection.
Delete student list
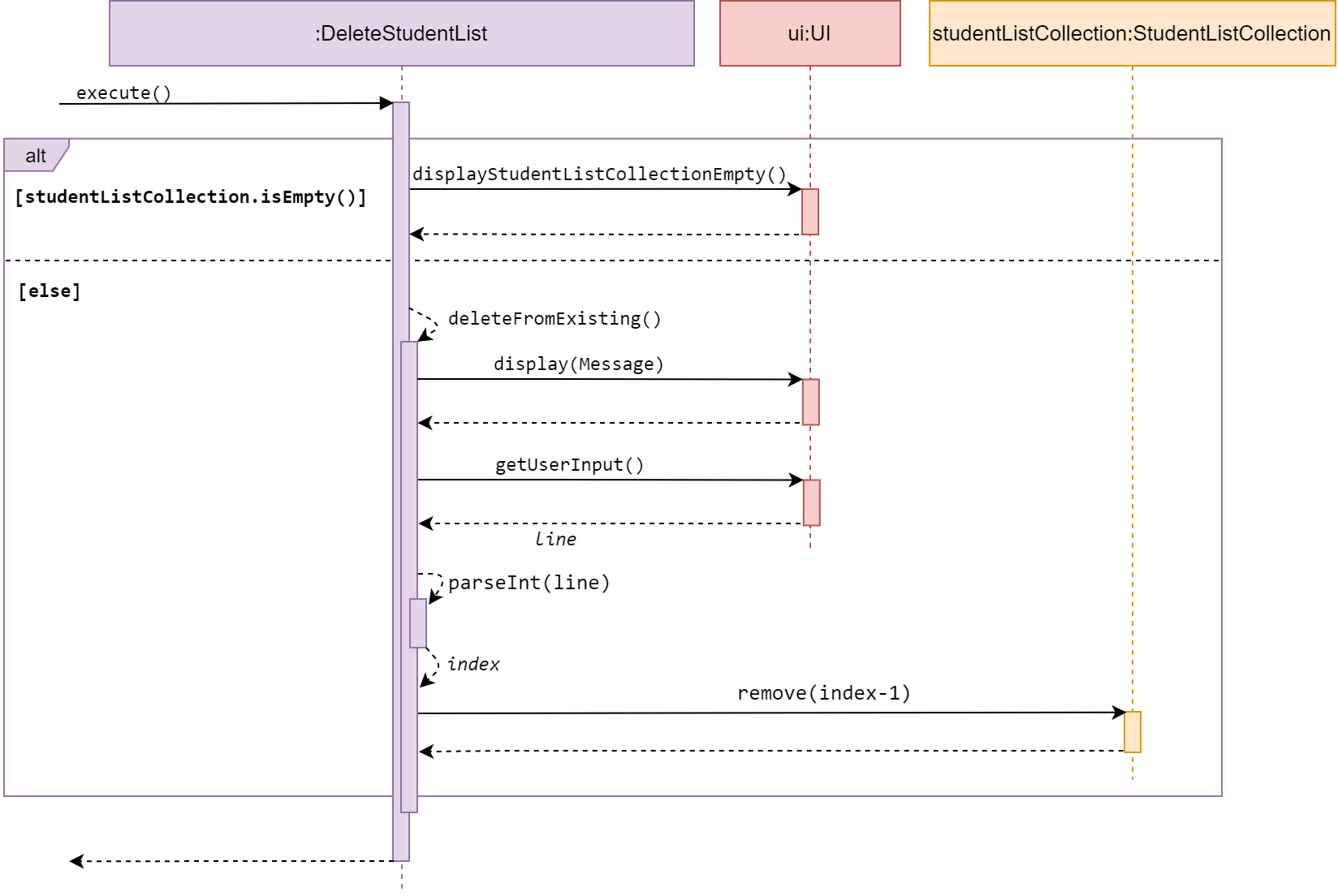
Sequence diagram of DeleteStudentList
DeleteStudentList is a subclass of Command. It allows the user to delete a student list
from the studentListCollection.
If the studentListCollection is empty, execute() calls displayStudentListCollectionEmpty()
form UI, to inform the user.
Else, it calls deleteFromExisting() from the same class and get user input for index, the
list number to be deleted.
The (index-1)th list in studentListCollection is deleted.
Clear student list
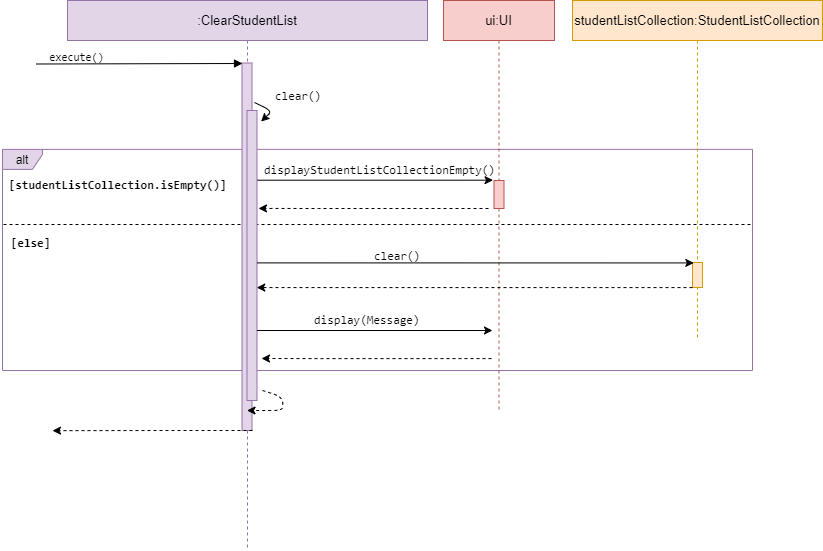
Sequence diagram of ClearStudentList
ClearStudentList is a subclass of Command. It allows the user to clear the
studentListCollection.
The method execute() calls clear() from the same class.
If the studentListCollection is empty, clear() calls displayStudentListCollectionEmpty()
from UI, to inform the user.
Else, it calls clear() from StudentListCollection to clear the collection.
The user will get informed when a success clear has been performed.
View student list
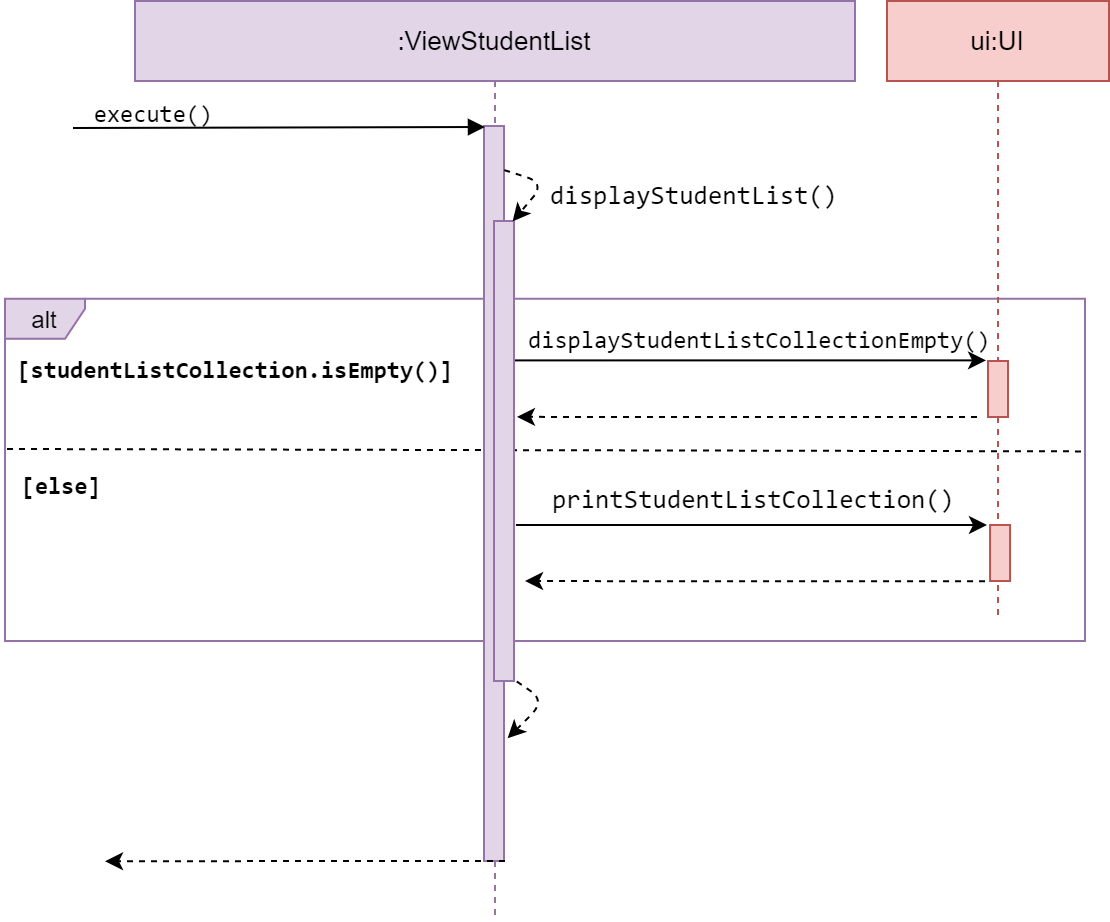
Sequence diagram of ViewStudentList
ViewStudentList is a subclass of Command. It allows the user to view a self
generated table based on the data in studentListCollection.
The method execute() calls displayStudentList() from the same class.
If the studentListCollection is empty, displayStudentList() calls
displayStudentListCollectionEmpty() from UI, to inform the user.
Else, it calls printStudentListCollection() from UI to print the table.
Find student list
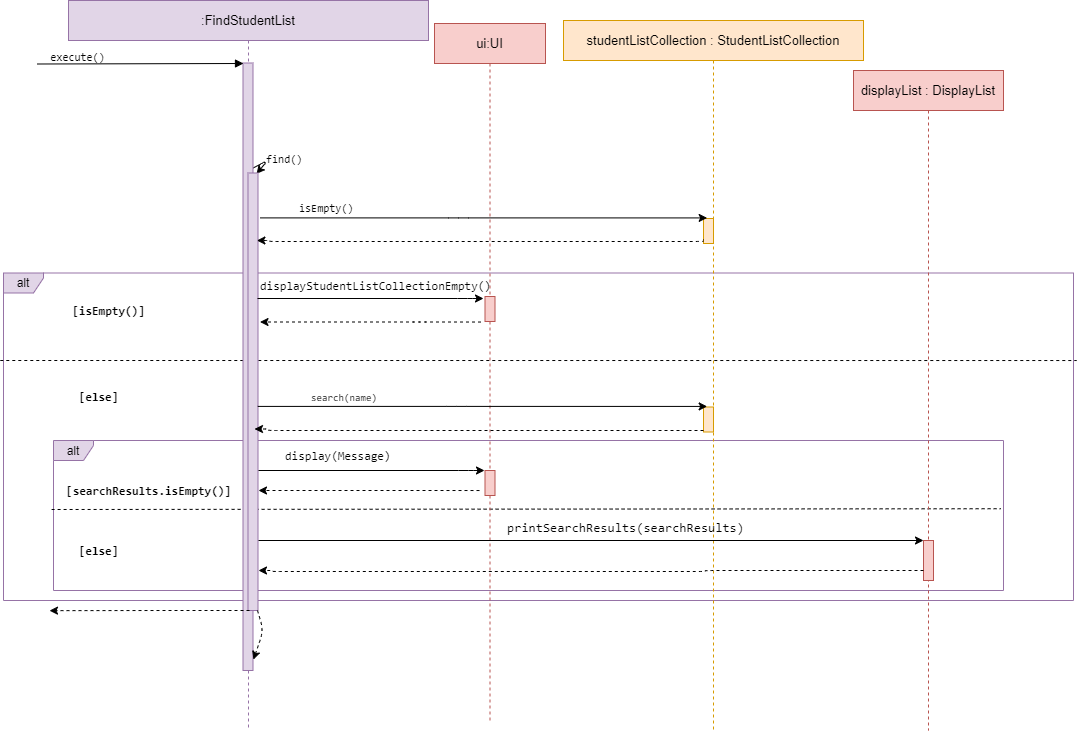
Sequence diagram of FindStudentList
FindStudentList is a subclass of Command. It allows the user to find a certain studentList
in studentListCollection.
The method execute() calls find() from the same class.
If the studentListCollection is empty, displayStudentList() calls
displayStudentListCollectionEmpty() from UI, to inform the user.
Else, it calls displayStudentListCollection() from the same class to print the table.
Next, it will prompt the user for a keyword. Using the keyword, it will iterate through
the studentListCollection to find a studentListCollection listName that equals to the keyword.
Last, it will call printSearchResults from displayList to display the searchResults found.
The user will get informed when a success sort has been performed.
Sort student list
-
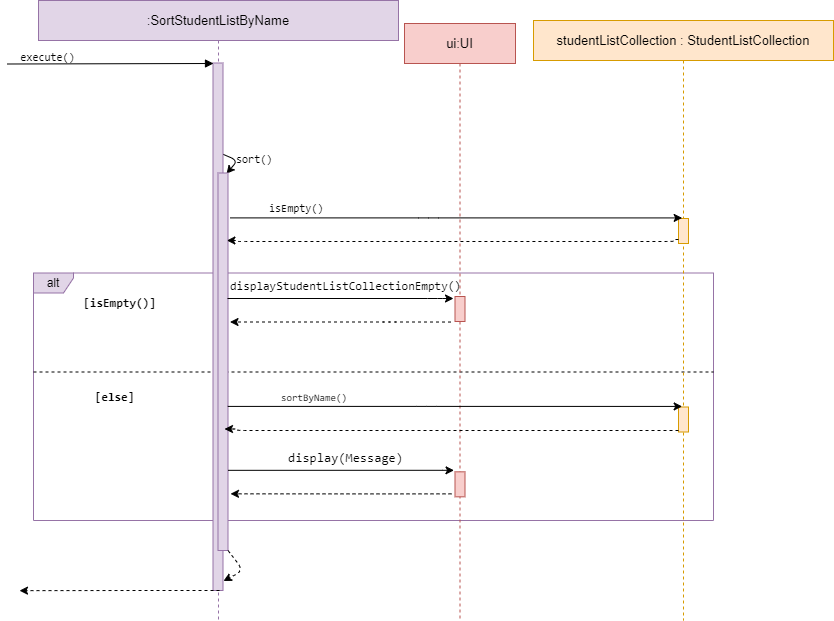
Sequence diagram of SortStudentListByName -
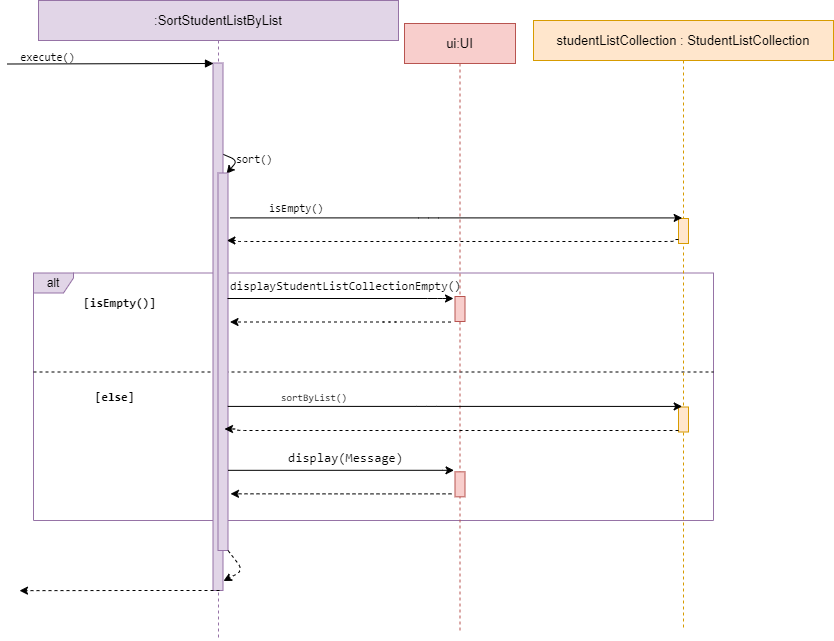
Sequence diagram of SortStudentListByList
SortStudentListByName and SortStudentListByList are subclasses of Command.
They both allow the user to sort a student list by either the student’s name within a list or
the list name of studentList stored within the studentListCollection.
The two Commands will be discussed together in this section as they have similar behaviour.
The methods SortStudentListByName and SortStudentListByList access a desired studentListCollection and
check whether the collection is empty.
If empty, it calls display() in UI and inform the user list is empty.
Else, it will sort the studentListCollection or studentList by the type mentioned in its method name.
3.6 Help
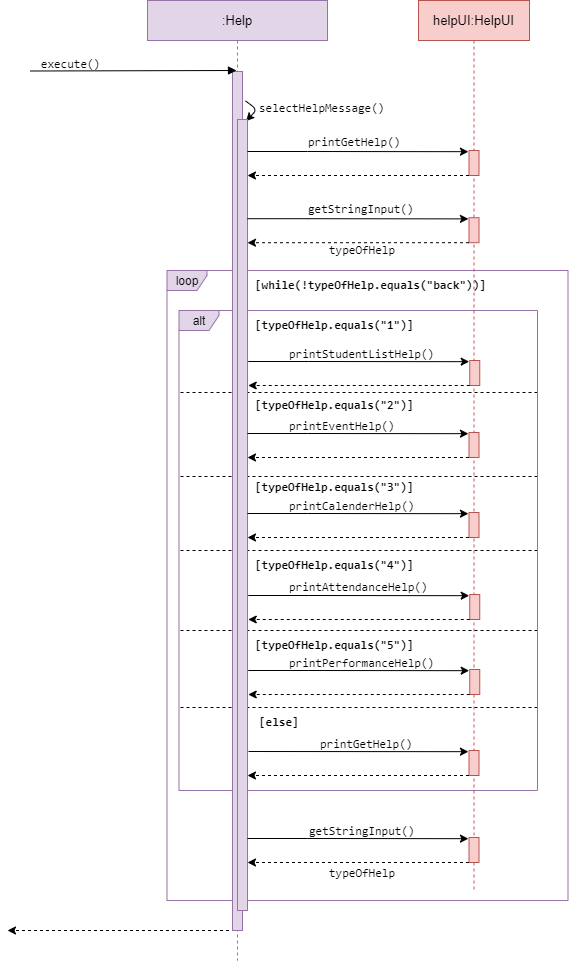
Sequence diagram for Help
Help function provides a summary of command format for the user.
When help command is executed, a menu page is shown at the console.
It then calls getStringInput() from UI, to get user input, typeOfHelp, and prints
corresponding help information to user.
Appendix
Appendix A: Target user profile
Our target audiences are professors who need help organizing their personal work schedule and need more time. The professors are pressed for time and they require a simple software to organize their monthly events and keep track of their students’ attendance and performance.
Appendix B: Value proposition
Our application will reduce the stress of the professor by allowing them to easily enter and store their work schedule as well as their students’ records. After storing the data, the Professor can have quick access to the information in either a list or a calendar view.
Appendix C: Non-Functional Requirements
- Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java 11 or above installed.
- Should be able to hold up to 1000 events without a noticeable sluggishness in performance for typical usage.
- A user with above average typing speed for regular English text (i.e. not code, not system admin commands) should be able to accomplish most of the tasks faster using commands than using the mouse.
{More to be added in future revisions}
Appendix D: User Stories
| Version | As a … | I want to … | So that I can … |
|---|---|---|---|
| v1.0 | professor | add new events | creating new events |
| v1.0 | professor | delete existing events | delete unnecessary events |
| v1.0 | professor | add new attendance list | create new attendance list to be added to events |
| v1.0 | professor | delete existing attendance list | delete unnecessary attendance list |
| v1.0 | professor | add new performance list | create new performance list to be added to events |
| v1.0 | professor | delete existing performance list | delete unnecessary performance list |
| v1.0 | professor | add date and time to my events | organize my events |
| v1.0 | professor | add venue to my events | locate events |
| v1.0 | professor | edit my events | update my existing events |
| v2.0 | professor | create a student list | link existing student list to performance list or attendance list |
| v2.0 | professor | Create repeatable events without having the need to manually add in | easily create occurring events |
| v2.0 | professor | find an event by name | locate an event without having to go through the entire list |
| v2.0 | professor | view calendar of all my events | to see a overview of them |
| v2.1 | professor | edit my student’s attendance | update my existing student’s attendance |
| v2.1 | professor | find my student’s attendance | locate an existing student’s attendance |
Appendix E: Instructions for Manual Testing
Set up
- Download the jar file and copy it into an empty folder.
- Run the jar file by typing java -jar Pac-2.1.jar after going into the file’s home directory folder in command terminal.
Adding an event
- Prerequisite: None
- Test case:
event add n/1 v/2 d/2000-01-01 t/0000
Expected: An event is added with name, venue and datetime. - Test case:
event add n/1 v/2
Expected: An event is added without datetime. A warning message about unknown datetime is shown. - Test case:
event add n/1 d/2000-01-01 t/0000
Expected: An event is added without venue. - Test case:
event add n/1
Expected: An event is added with only name. A warning message about unknown datetime is shown. - Test case:
event add v/2
Expected: An event is added with default name and no datetime. A warning message about unknown datetime is shown. - Test case:
event add d/2000-01-01 t/0000(no name and venue)
Expected: No event is added. Error details shown. - Test case:
event add n/(only flag, no parameter)
Expected: No event is added. Error details shown. - Other incorrect commands to try:
- either date or time, but not both, is given
- adding something before flag
Deleting an event
- Prerequisites: At least one event must be added beforehand.
- Test case:
event delete i/1
Expected: First event is deleted from the list. The name of the deleted event is shown. - Test case:
event delete i/0(or other index that is less than 1)
Expected: No event is deleted. Error details shown. - Test case:
event delete i/10(out of bound)
Expected: No event is deleted. Error details shown. - Test case:
event delete i/apple(not an integer)
Expected: No event is deleted. Error details shown. - Test case:
event delete 1(too short to look for flag)
Expected: No event is deleted. Error details shown. - Test case:
event delete apple(no flag)
Expected: No event is deleted. Error details shown.
Saving and loading corrupted data
- Make sure you have some events and/or student lists to load.
- You can use
event add, andstudentlist addto add some.
- You can use
- Close the application using
byecommand.All events are saved.is shown if there are events to save.All student lists are saved.is shown if there are student lists to save.- They are saved under
data/.
- Delete all commas and pipes under
eventlist.txtto simulate data corruption. - Run the application again.
- You will see
...Corrupted event found. Only previous events are loaded. - If you have unmodifed events before the corrupted event, they will be loaded and saved.
Follow all-in-one command for following commands:
Event
- Add an event by typing
event add n/NAME - View the populated events by typing
event list - View the populated seminars by typing
seminar list - Delete an event by typing
delete i/INDEX - Edit an existing event’s name by typing
event editname i/INDEX n/NAME - Edit an existing event’s date and time by typing
event editdatetime i/INDEX d/DATE t/TIME - Edit an existing event’s venue by typing
event editvenue i/INDEX v/VENUE
Calender
- Add an event with date and time
event add n/work d/2020-04-05 t/1230 - Display calendar by entering
calendar s/2 ay/19-20
Follow step-by-step command in console for following commands:
Attendance
- Add attendance to attendance list by typing
attendance add - Clear attendance list by typing
attendance clear - View generated table for attendance list by typing
attendance view - Sort attendance list by typing
attendance sort - Find attendance by typing
attendance find - Edit attendance by typing
attendance edit
Performance
- Add performance to performance list by typing
performance add - Delete a performance from performance list by typing
performance delete - View generated table for performance list by typing
performance view - Edit performance list by typing
performance edit - Sort performance list by typing
performance sort
Student name list
- Add name to student name list by typing
studentlist add - Delete name from student name list by typing
studentlist delete - View generated table for student name list by typing
studentlist view - Find a student name in student name list by typing
studentlist find - Sort student list by typing
studentlist sort
Glossary
- mainstream OS - Windows, Linux, Unix, OS-X
- flag - anything that takes the form of
?/, e.g.n/,i/ - student list - a list of students’ name
- student list collection - a collection of list of students’ name
- attendance - a combination of student’s name and attendance status
- attendance list - a list of students’ name and attendance status
- performance - a combination of students’ name and result
- performance list - a list of students’ name and result
- Calendar - Display columns of event in a chosen semester, each column represents a month in the chosen semester